In today’s rapidly changing world, the concept of sustainability has gained significant importance. As governments and organizations strive to address the pressing issues of climate change, social inequality, and economic instability, the triple bottom line approach has emerged as a comprehensive framework for achieving long-term sustainability and societal well-being.
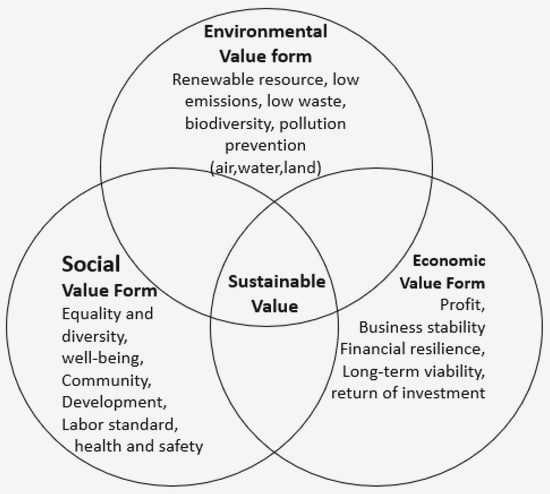
At its core, the triple bottom line approach considers three key dimensions: environmental, social, and economic. It recognizes that for a civilization to thrive, it must not only prioritize environmental conservation, but also ensure the well-being of its citizens and maintain a flourishing economy that benefits all stakeholders.
Implementing the triple bottom line approach requires a holistic and integrated approach across various sectors of civil society. Governments, non-profit organizations, businesses, and communities must all play a role in promoting sustainable practices and fostering a culture of responsible decision-making.
From an environmental perspective, this entails reducing carbon emissions, conserving natural resources, and promoting renewable energy. Socially, it involves fostering inclusivity, promoting social justice, and improving access to education, healthcare, and basic necessities for all members of society. Economically, it means embracing sustainable business practices, supporting fair trade, and investing in innovative solutions that create long-term value without compromising future generations’ ability to thrive.
By adopting the triple bottom line approach, civil society can pave the way for a sustainable future. It offers a framework for decision-making that goes beyond short-term gains, encouraging organizations and individuals to consider the broader impacts of their actions and make choices that contribute to the well-being of both current and future generations.
Understanding the Triple Bottom Line Approach
The triple bottom line approach is a framework that evaluates the performance of an organization in three key areas: economic, social, and environmental. This approach recognizes that a sustainable future requires a balance between these three pillars of success.
Economic
The economic aspect of the triple bottom line approach assesses the financial performance and profitability of an organization. It considers factors such as revenue, costs, and investments to determine whether the organization is economically sustainable. A key goal in the economic aspect is to generate long-term value and ensure the financial viability of the organization.
Social
The social aspect focuses on the impact of an organization on society and its stakeholders. It considers factors such as employee well-being, community engagement, and ethical practices. This aspect recognizes the importance of building strong relationships with stakeholders and promoting social equity and justice.
Environmental
The environmental aspect evaluates the impact of an organization on the natural environment. It considers factors such as resource consumption, waste management, and carbon footprint. This aspect aims to minimize negative environmental impacts and promote sustainability by adopting practices that reduce resource use and pollution.
By adopting the triple bottom line approach, organizations can ensure that they are not only financially successful but also socially responsible and environmentally conscious. This approach promotes a holistic view of sustainability and encourages organizations to consider the long-term consequences of their actions on all aspects of society.
The Importance of Sustainability in Civil Society
Sustainability is a vital aspect of civil society that cannot be overlooked. It is the key to ensuring a better future for both current and future generations. With the excessive exploitation of natural resources and the increasing impact of human activities on the environment, sustainability plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance between social, environmental, and economic factors.
Social Impact
A sustainable civil society promotes social well-being by emphasizing equity, inclusivity, and social justice. It focuses on meeting the needs of all community members, particularly those who are marginalized or disadvantaged. By providing access to basic services, education, healthcare, and equal opportunities, sustainability fosters a society where everyone can thrive and contribute to its development.
Environmental Protection
Preserving the environment is a fundamental pillar of sustainability in civil society. It involves reducing pollution, conserving natural resources, and protecting biodiversity. By implementing environmentally friendly practices, such as waste reduction, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable land use, civil society can help mitigate climate change and minimize its ecological footprint.
Economic Resilience
Sustainability in civil society also plays a crucial role in building economic resilience. By promoting sustainable entrepreneurship and responsible business practices, it creates opportunities for economic growth while ensuring long-term viability. This approach encourages innovation, resource efficiency, and the development of sustainable industries that can withstand environmental challenges and economic uncertainties.
In conclusion, sustainability is of utmost importance in civil society. It promotes social well-being, protects the environment, and enhances economic resilience. By adopting a triple bottom line approach that considers people, planet, and profit, civil society can create a sustainable future that benefits everyone. It requires collaboration, commitment, and a shift towards sustainable practices in all aspects of life to achieve a better and more equitable world for generations to come.
The Economic Component of the Triple Bottom Line
The economic component of the triple bottom line refers to the financial impact of an organization’s activities and initiatives. It focuses on generating profit, increasing revenue, and ensuring overall economic growth. This component recognizes that financial success is essential for the long-term sustainability of an organization and its ability to fulfill its social and environmental responsibilities.
Financial viability is a key aspect in the economic component. Organizations need to generate enough revenue to cover their expenses and ensure profitability. This includes careful financial planning, budgeting, and investment decisions. By effectively managing their finances, organizations can contribute to economic stability and growth in the communities they operate in.
Investment in innovation is another crucial element of the economic component. In order to stay competitive and adapt to changing market conditions, organizations must invest in research and development, technological advancements, and process improvements. These investments not only help organizations achieve cost efficiency and gain a competitive edge, but also contribute to economic growth by fostering innovation and job creation.
Creating employment opportunities is an important part of the economic component. Organizations that prioritize job creation and provide fair wages and benefits contribute to the well-being and prosperity of their employees, as well as the local and national economy. By employing local talent, organizations can help boost employment rates and reduce poverty.
Responsible supply chain management is an essential consideration in the economic component. Organizations need to ensure that their supply chains are ethical, transparent, and sustainable. This involves selecting suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices, environmentally friendly production methods, and responsible sourcing of raw materials. By supporting responsible supply chain practices, organizations contribute to economic development while minimizing negative social and environmental impacts.
The Social Component of the Triple Bottom Line
The social component of the triple bottom line approach focuses on the impact that an organization has on society. It takes into consideration the well-being of employees, the community, and society as a whole. This component recognizes that businesses and civil society organizations have a responsibility to contribute positively to society and address social issues.
Employee well-being: The social component of the triple bottom line emphasizes the importance of creating a positive work environment for employees. This includes providing fair wages, ensuring equal opportunities for advancement, and promoting work-life balance. Organizations that prioritize employee well-being not only create a happier and healthier workforce, but also increase productivity and retention rates.
Community engagement: Another key aspect of the social component is community engagement. Organizations can contribute to their communities by supporting local initiatives, investing in infrastructure, and participating in community development projects. By engaging with the community, organizations can build trust and establish long-term relationships with stakeholders.
Social impact: The social component also focuses on the social impact that an organization has on society. This includes addressing social issues such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. Organizations can integrate social impact into their business models by developing sustainable products or services, implementing ethical sourcing practices, and supporting social causes through partnerships and donations.
Transparency and accountability: In order to fully embrace the social component of the triple bottom line, organizations must be transparent and accountable for their actions. This includes being open about their social impact, engaging in dialogue with stakeholders, and regularly reporting on their progress. By being transparent and accountable, organizations can build trust and credibility, and drive positive change within society.
Conclusion: The social component of the triple bottom line is a crucial aspect of creating a sustainable future. By prioritizing employee well-being, engaging with the community, addressing social issues, and being transparent and accountable, organizations can contribute positively to society and build a more sustainable and equitable future. By taking into consideration the social component alongside the environmental and economic components, organizations can achieve long-term success while also making a positive impact on people and the planet.
The Environmental Component of the Triple Bottom Line
The environmental component of the triple bottom line approach in civil society focuses on the impact of actions and decisions on the natural world. It recognizes that human activities have the potential to harm ecosystems and deplete natural resources, and aims to minimize these negative effects.
Environmental sustainability is a key element of the triple bottom line, as it emphasizes the need to protect and preserve the environment for future generations. This involves adopting sustainable practices that reduce pollution, conserve resources, and promote biodiversity.
Key considerations in the environmental component include:
- Climate change mitigation: Organizations implementing the triple bottom line approach recognize the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing down the pace of global warming. This can be achieved through measures such as using renewable energy sources, implementing energy efficiency measures, and adopting carbon offset programs.
- Waste management: Minimizing waste generation and implementing effective waste management strategies are crucial in achieving environmental sustainability. This involves adopting recycling and composting programs, reducing single-use plastics, and implementing sustainable packaging practices.
- Conservation of natural resources: The triple bottom line approach emphasizes the importance of conserving natural resources such as water, forests, and minerals. This can be achieved through measures such as implementing water conservation practices, promoting sustainable forestry practices, and emphasizing responsible mining and extraction techniques.
- Biodiversity preservation: Protecting and preserving biodiversity is an essential aspect of the environmental component. This involves conserving habitats, preventing species extinction, and promoting sustainable land use practices that maintain ecological balance.
By incorporating the environmental component into the triple bottom line approach, civil society organizations can contribute to the creation of a sustainable future by minimizing their environmental footprint and promoting responsible environmental practices.
Benefits of Implementing the Triple Bottom Line Approach
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) approach is a framework that encourages organizations to consider the economic, environmental, and social impacts of their activities. By implementing the TBL approach, civil society organizations can bring about several benefits.
1. Improved Environmental Sustainability
Implementing the TBL approach enables organizations to assess and minimize their environmental impact. By evaluating resource usage, waste generation, and emissions, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement sustainable practices. This leads to reduced environmental degradation, conservation of resources, and the preservation of ecosystems for future generations.
2. Enhanced Social Responsibility
The TBL approach promotes social responsibility by encouraging organizations to prioritize the well-being of their stakeholders and the broader community. By considering social factors such as labor conditions, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement, organizations can contribute to the development and support of local communities. This results in improved relationships with stakeholders, increased employee satisfaction, and a positive organizational reputation.
3. Financial Stability and Long-term Success
Implementing the TBL approach can lead to financial stability and long-term success for organizations. By considering the economic impacts of their actions, organizations can identify opportunities for cost savings, resource efficiency, and innovation. Moreover, integrating sustainability into the organizational strategy can enhance brand value, attract investors and customers who value sustainability, and create a competitive advantage in the market.
4. Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration
The TBL approach fosters stakeholder engagement and collaboration by involving various stakeholders in the decision-making process. By considering the perspectives and needs of different stakeholders, organizations can build stronger relationships, gain valuable insights, and create mutually beneficial partnerships. This leads to more effective problem-solving, increased trust, and shared responsibility in achieving sustainable goals.
5. Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Implementing the TBL approach helps organizations comply with regulations and standards related to sustainability. By monitoring and reporting on their environmental and social practices, organizations can demonstrate transparency and accountability. This not only helps avoid legal and reputational risks but also positions organizations as responsible and trustworthy entities in the eyes of regulators, customers, and the public.
Overall, implementing the Triple Bottom Line approach can bring numerous benefits to civil society organizations, ranging from improved environmental sustainability and social responsibility to financial stability and stakeholder engagement. By embracing this holistic approach, organizations can contribute to creating a sustainable future for all.
Examples of Successful Implementation in Civil Society
Civil society organizations are at the forefront of implementing the triple bottom line approach to create a sustainable future. Here are some examples of successful implementation in civil society:
1. Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives
Numerous civil society organizations have successfully implemented sustainable agriculture initiatives. These initiatives focus on promoting organic farming practices, reducing the use of chemical inputs, and implementing agroecological principles. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices, these organizations are not only preserving the environment but also improving the quality and safety of food.
2. Community-Based Renewable Energy Projects
Civil society organizations are also leading the way in implementing community-based renewable energy projects. These projects involve the installation and operation of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies at the community level. By harnessing clean and renewable energy sources, these projects contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and promote energy independence.
3. Zero Waste Campaigns
Another example of successful implementation in civil society is the adoption of zero waste campaigns. These campaigns aim to reduce waste generation and promote recycling and composting. Civil society organizations work with local communities, businesses, and governments to implement waste reduction and resource recovery initiatives. Through education and awareness campaigns, these organizations help shift attitudes and behaviors towards a more sustainable waste management system.
4. Responsible Investment Practices
Civil society organizations are actively pushing for responsible investment practices. They advocate for divestment from fossil fuels and support investments in sustainable industries and projects. By engaging with investors, policymakers, and the public, these organizations encourage the adoption of social and environmental criteria in investment decision-making, leading to a more sustainable allocation of resources.
These examples demonstrate how civil society organizations are actively implementing the triple bottom line approach and making significant contributions to creating a sustainable future. Through their initiatives and campaigns, they are promoting environmental stewardship, social equity, and economic prosperity.
Challenges and Obstacles to Implementing the Triple Bottom Line Approach
Implementing the triple bottom line approach in civil society comes with its fair share of challenges and obstacles. One of the main challenges is shifting the mindset and values of individuals and organizations towards considering not just financial profitability, but also social and environmental impacts. This requires a significant cultural shift and a change in the way individuals and institutions perceive success and measure value. It can be difficult to convince stakeholders who are mostly concerned with short-term financial gains to embrace a broader perspective that takes into account the triple bottom line.
Another obstacle to implementing the triple bottom line approach is the lack of standardized metrics and evaluation tools. While there are various frameworks and guidelines available for measuring social and environmental impacts, there is no universal system that is widely accepted and adopted. This lack of consistency makes it challenging to compare and benchmark performance across different organizations and sectors, hindering the ability to assess progress and make informed decisions.
Additionally, the allocation of resources and funding can pose a significant challenge. Implementing the triple bottom line approach often requires upfront investments in new technologies, processes, and infrastructure, which can be costly. Many organizations may be unwilling or unable to allocate the necessary resources, especially if they do not see immediate financial returns. Furthermore, the lack of financial incentives and regulatory frameworks that reward sustainable practices can discourage organizations from adopting the triple bottom line approach.
Resistance to change is another obstacle that organizations may face when implementing the triple bottom line approach. Some stakeholders may resist the shift towards sustainability due to fear of the unknown, skepticism about the effectiveness of sustainable practices, or concerns about the disruption it may cause to existing systems and processes. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, education, and collaboration to build trust and demonstrate the benefits of the triple bottom line approach.
In conclusion, implementing the triple bottom line approach in civil society is not without its challenges. Shifting mindsets, lack of standardized metrics, resource allocation, and resistance to change are some of the major obstacles that organizations may encounter. However, with proper education, collaboration, and supportive policies, these challenges can be overcome, leading to a more sustainable future for society.
Best Practices for Implementing the Triple Bottom Line Approach
1. Establish Clear Sustainability Goals
Before implementing the triple bottom line approach, it is important to establish clear sustainability goals that align with the organization’s mission and values. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By clearly defining what the organization aims to achieve in terms of environmental, social, and economic sustainability, it becomes easier to develop strategies and measures to track progress.
2. Integrate Sustainability into Decision-Making Processes
Sustainability should be integrated into the organization’s decision-making processes at all levels. This means considering the social, environmental, and economic impacts of decisions before they are made. By adopting a holistic approach and considering the triple bottom line, organizations can make more informed and sustainable choices that take into account the long-term consequences of their actions.
3. Engage Stakeholders
Engaging stakeholders is crucial for the successful implementation of the triple bottom line approach. Stakeholders include employees, customers, suppliers, local communities, and other relevant parties. By involving stakeholders in decision-making processes and seeking their input and feedback, organizations can gather diverse perspectives and ensure that their sustainability initiatives align with the needs and expectations of all stakeholders.
4. Measure and Track Progress
In order to assess the effectiveness of the triple bottom line approach, it is important to measure and track progress regularly. This involves collecting data and metrics related to environmental, social, and economic performance. By monitoring key indicators, organizations can identify areas for improvement, set benchmarks, and evaluate the impact of their sustainability initiatives over time.
5. Collaborate and Share Best Practices
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for advancing sustainability goals. Organizations can benefit from collaborating with other like-minded organizations, sharing best practices, and learning from each other’s experiences. By joining networks, participating in forums, and sharing success stories, organizations can accelerate their progress towards achieving the triple bottom line and contribute to a more sustainable future for all.
Conclusion:
Implementing the triple bottom line approach requires a comprehensive and integrated approach that involves setting clear goals, integrating sustainability into decision-making processes, engaging stakeholders, measuring and tracking progress, and collaborating with others. By following these best practices, organizations can contribute to a more sustainable future and create lasting positive impacts in their communities and beyond.





