Program evaluation plays a crucial role in the success of civil society organizations. It helps to assess the effectiveness and impact of programs and initiatives, and enables organizations to make data-driven decisions for improvement and growth. However, evaluating programs can be a complex and challenging process that requires careful planning, implementation, and analysis.
One of the key best practices for program evaluation in civil society is the establishment of clear evaluation goals and objectives. This involves identifying what needs to be evaluated, why it needs to be evaluated, and what outcomes or changes the organization hopes to achieve. By setting these goals and objectives, organizations can ensure that the evaluation process is focused and aligned with their overall mission and strategic priorities.
Another important best practice is the selection of appropriate evaluation methods and tools. There are different evaluation approaches and techniques, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and document analysis, among others. The choice of methods should be based on the specific evaluation goals and objectives, as well as the available resources and constraints. It is also important to consider the perspectives and needs of all stakeholders, including program participants, staff, donors, and other relevant parties.
Furthermore, program evaluation should be conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner. This means following a logical sequence of steps, from planning and data collection, to analysis and reporting. It also involves using valid and reliable measures, ensuring data quality and integrity, and applying appropriate statistical and analytical techniques. By adhering to a systematic approach, organizations can obtain accurate and meaningful findings that can inform decision-making and program improvement.
In conclusion, program evaluation is a critical aspect of success for civil society organizations. By following best practices, such as establishing clear goals, selecting appropriate methods, and conducting evaluations systematically, organizations can effectively assess their programs and ensure that they are making a positive impact on the communities they serve.
The Importance of Program Evaluation
Program evaluation plays a crucial role in the success of any civil society initiative. It is an essential process that assesses the impact and effectiveness of programs, ensuring that they are achieving their desired outcomes. By evaluating programs, organizations can identify areas of strength and weakness, make informed decisions, and continuously improve their initiatives.
Evidence-based decision making: Program evaluation provides organizations with valuable evidence to make informed decisions. It helps identify what is working well and what is not, allowing organizations to focus their resources on effective strategies and address any challenges or gaps in their programs.
Accountability and transparency: Evaluation promotes accountability and transparency within civil society organizations by providing stakeholders with a clear understanding of how programs are performing and the impact they are having. It ensures that organizations are responsible for the resources they receive and provides evidence to donors, funders, and the public about the value and effectiveness of their investments.
Learning and improvement: Evaluation helps organizations learn from their experiences and improve their programs. By examining the outcomes and processes of their initiatives, organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement necessary changes, and enhance their ability to achieve their goals. Continuous evaluation allows for ongoing learning and adaptation, leading to more effective and impactful programs.
Strategic planning: Program evaluation provides vital information for strategic planning. It helps organizations identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, enabling them to develop or refine their strategies accordingly. Evaluation findings can inform the setting of realistic goals, the allocation of resources, and the development of action plans, ensuring that programs are aligned with the organization’s mission and objectives.
Collaboration and partnerships: Evaluation can foster collaboration and partnerships within the civil society sector. Sharing evaluation findings and best practices can enhance knowledge exchange, promote collective learning, and encourage collaboration between organizations working towards similar goals. By leveraging evaluation results, organizations can build stronger partnerships and create a more coordinated and impactful approach to address societal challenges.
Defining Program Evaluation
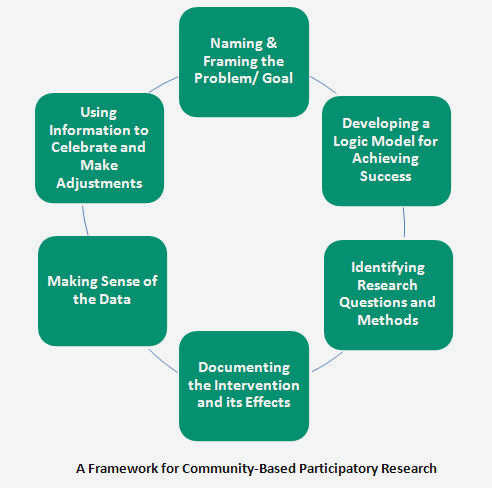
Program evaluation is a systematic process of assessing the design, implementation, and outcomes of a program or intervention. It involves gathering and analyzing data to determine the effectiveness, efficiency, and relevance of the program in achieving its intended goals and objectives.
Evaluating a program helps stakeholders, such as funders, program managers, and policymakers, make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, program improvements, and policy development. It provides insight into what is working well and what needs to be improved or changed to achieve better outcomes.
There are various approaches to program evaluation, including formative evaluation, which focuses on assessing program development and implementation, and summative evaluation, which examines program outcomes and impacts. The evaluation process typically involves identifying evaluation questions, collecting data, analyzing and interpreting the data, and reporting the findings to stakeholders.
Effective program evaluation requires the use of reliable and valid data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, observations, and document reviews. It also requires careful consideration of ethical considerations, such as ensuring participant confidentiality and informed consent. The findings of the evaluation should be communicated clearly and effectively to stakeholders to facilitate evidence-based decision-making.
Overall, program evaluation is essential for promoting accountability, learning, and improvement within civil society organizations. It helps organizations understand the impact of their programs, identify areas for improvement, and make evidence-based decisions for the benefit of their beneficiaries and stakeholders.
Setting Clear Goals and Objectives
Setting clear goals and objectives is a crucial step in program evaluation. Without clearly defined objectives, it becomes difficult to measure the success or failure of a program. Goals and objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They provide a clear direction and purpose for the evaluation process.
Specific: Goals and objectives should be clear and specific. They should clearly state what the program aims to achieve and provide a clear focus for the evaluation.
Measurable: Goals and objectives should be quantifiable, or at least have some form of measurement attached to them. This allows for the evaluation to assess the extent to which the program has achieved its desired outcomes.
Achievable: Goals and objectives should be realistic and attainable. They should take into consideration the available resources and capacities of the program. Unrealistic goals will only lead to frustration and a lack of motivation for evaluation.
Relevant: Goals and objectives should be relevant to the program and its intended outcomes. They should address the key issues and problems that the program aims to solve. Relevant goals ensure that the evaluation focuses on the most important aspects of the program.
Time-bound: Goals and objectives should have a specific time frame attached to them. This helps in tracking the progress of the program over time and allows for a comparison between the planned objectives and the actual outcomes.
In conclusion, setting clear goals and objectives is essential for a successful program evaluation. It provides a clear direction and purpose for the evaluation process and ensures that the evaluation focuses on the most important aspects of the program. By following the SMART criteria, organizations can set realistic and measurable goals that will contribute to the overall success of the program.
Collecting and Analyzing Data
When conducting a program evaluation in civil society, it is essential to gather and analyze data effectively. Collecting accurate and relevant data is crucial to understanding the impact and effectiveness of a program. Data collection methods may vary depending on the nature of the program and the evaluation goals, but there are some best practices that can be followed.
Data collection methods: One common method is surveys, which can be conducted with program participants, staff, or other stakeholders. Surveys can provide quantitative data and help assess participants’ perceptions and experiences. Another method is interviews, which allow for more in-depth qualitative data collection, capturing personal stories and insights. Additionally, focus groups can be used to gather feedback and engage participants in a group discussion format.
Data analysis: Once data is collected, it is important to analyze it effectively. This involves organizing and summarizing the data to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Quantitative data can be analyzed using statistical techniques, such as calculating averages or conducting regression analysis. Qualitative data, on the other hand, can be analyzed through coding and thematic analysis, identifying key themes or categories within the data. Combining both quantitative and qualitative data analysis methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the program’s impact.
Data quality: Ensuring data quality is crucial to the success of a program evaluation. This includes using reliable measurement tools, minimizing bias in data collection methods, and conducting data validation checks. It is important to document data collection procedures and ensure data is securely stored to maintain integrity and confidentiality.
Reporting and communication: Once data is analyzed, it is essential to effectively communicate the findings to stakeholders. Reports should be clear, concise, and tailored to the target audience. Visual aids, such as charts or graphs, can help convey complex data in an easily understandable format. Engaging stakeholders throughout the evaluation process and involving them in the interpretation of findings can foster buy-in and ensure the evaluation’s impact on decision-making.
In conclusion, collecting and analyzing data is a critical step in program evaluation in civil society. By following best practices and using appropriate methods, data can provide valuable insights into a program’s impact and effectiveness. Effective communication of findings is essential to ensure that the evaluation influences decision-making and drives positive change.
Using Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
When evaluating programs in civil society, it is essential to use both quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of impact and effectiveness. Quantitative methods involve the collection and analysis of numerical data, while qualitative methods involve the collection and analysis of non-numerical data, such as interviews, observations, and case studies.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods provide measurable data that can be analyzed statistically. These methods often involve surveys, questionnaires, and statistical analysis of data collected from large sample sizes. The use of quantitative methods allows evaluators to measure the extent of program outcomes, such as the number of participants, the level of satisfaction, or the change in knowledge or behavior.
One common quantitative method is a pre and post-test design, where participants are assessed before and after the program to measure the change in outcomes. Surveys with Likert scale questions are also commonly used to collect quantitative data on participant attitudes and opinions. These methods provide valuable data that can be used to identify patterns, make comparisons, and draw statistical conclusions.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods provide in-depth insights and understanding of program processes, experiences, and contextual factors. These methods often involve interviews, focus groups, participant observations, and document analysis. By collecting qualitative data, evaluators can explore the motivations, perceptions, and experiences of participants and other stakeholders.
Interviews and focus groups allow evaluators to have direct interactions with participants, allowing for the exploration of complex issues and capturing diverse perspectives. Participant observations and document analysis can provide valuable context for understanding program implementation and uncovering unintended outcomes or unexpected challenges.
Combining quantitative and qualitative methods allows for a more complete and nuanced understanding of program outcomes. Quantitative methods provide statistical evidence of impact, while qualitative methods offer insights into the processes and mechanisms that contribute to these outcomes. By utilizing both methods, evaluators can provide a comprehensive evaluation that aids in program improvement and decision-making.
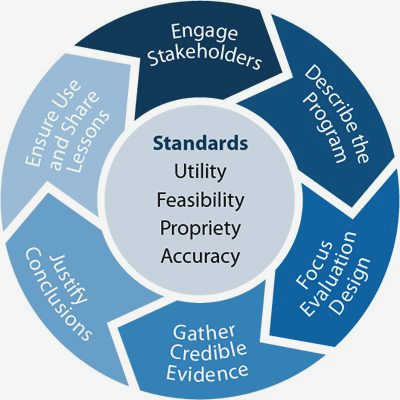
Engaging Stakeholders
Why Engage Stakeholders?
Engaging stakeholders is a crucial step in the program evaluation process. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the program being evaluated, such as donors, beneficiaries, staff, and community members. Their involvement ensures that the evaluation is comprehensive, inclusive, and representative of all perspectives.
Identifying Stakeholders
In order to effectively engage stakeholders, it is necessary to identify and understand who they are. This can be done by conducting a stakeholder analysis, which involves mapping out key individuals and groups, and assessing their level of interest and influence in the program. This analysis helps in prioritizing stakeholders for engagement and ensuring that all relevant voices are heard.
Methods of Engagement
There are various methods that can be used to engage stakeholders in the evaluation process. These can include surveys, interviews, focus groups, workshops, and feedback sessions. It is important to choose methods that are appropriate for the stakeholders involved and to provide opportunities for both online and offline engagement. Additionally, clear communication channels should be established to facilitate ongoing dialogue and information sharing.
Benefits of Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders has numerous benefits for the program evaluation process. Firstly, it promotes transparency and accountability, as stakeholders are able to provide input and hold the program accountable for its outcomes. Secondly, it helps to build trust and buy-in from the stakeholders, as their perspectives and experiences are valued. Lastly, stakeholder engagement leads to more meaningful and actionable evaluation findings, as it ensures that the evaluation is grounded in the realities and needs of those directly affected by the program.
Challenges and Considerations
While stakeholder engagement is important, it can also present challenges. One challenge is ensuring equal representation and participation from all stakeholders, particularly marginalized groups or those with limited resources. Language and cultural barriers may also need to be addressed in order to ensure meaningful engagement. In addition, it is important to consider power dynamics and be mindful of any potential conflicts of interest that may arise during the engagement process.
Ensuring Ethical Practices
Transparent and accountable process
Ensuring ethical practices in program evaluation involves maintaining a transparent and accountable process. This includes clearly documenting the objectives and methods of the evaluation, as well as the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved. A transparent process allows stakeholders to have a clear understanding of how decisions are made and how data is collected, analyzed, and reported. This helps build trust and ensures that the evaluation is conducted in an ethical manner.
Informed consent
Obtaining informed consent is an important ethical consideration in program evaluation. This means that participants should be fully informed about the purpose of the evaluation, the methods used, and any potential risks or benefits. Participants should have the opportunity to ask questions and provide consent voluntarily, without any coercion or pressure. Informed consent ensures that participants are aware of their rights and that their confidentiality and privacy are protected throughout the evaluation process.
Confidentiality and anonymity
Maintaining confidentiality and anonymity is essential in program evaluation to ensure ethical practices. Evaluators should take measures to protect the identity of participants and ensure that their personal information is held securely. This includes using codes or pseudonyms to identify participants instead of their actual names. By safeguarding confidentiality and anonymity, evaluators can create a safe and trusted environment for participants to provide honest and accurate information without fear of repercussions.
Ethical data handling and analysis
Ethical data handling and analysis is another important aspect of ensuring ethical practices in program evaluation. Evaluators should collect, store, and analyze data in a way that respects the privacy and confidentiality of participants. This includes using secure methods for data storage and ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to the data. Evaluators should also use appropriate methods and techniques for data analysis, ensuring that the results are reliable, valid, and unbiased.
Conflict of interest
Managing conflicts of interest is crucial in program evaluation to maintain ethical practices. Evaluators should disclose any potential conflicts of interest that may arise during the evaluation process. This includes any personal or financial relationships that could influence their objectivity or decision-making. By openly addressing and managing conflicts of interest, evaluators can ensure that the evaluation is conducted impartially and without bias.
Ongoing evaluation and improvement
Ethical practices in program evaluation also involve ongoing evaluation and improvement of the evaluation process itself. This includes regularly reviewing and reflecting on the methods and procedures used, as well as seeking feedback from stakeholders. By continuously striving to improve the evaluation process, evaluators can ensure that ethical standards are upheld, and that the evaluation is rigorous, valid, and reliable.
Applying Evaluation Results for Program Improvement
Using evaluation findings to inform program design
When conducting program evaluations, it is crucial to apply the results in order to improve program design and effectiveness. By analyzing the data gathered during evaluation, organizations can identify areas of strength and areas for improvement.
Identifying program strengths:
- Evaluation findings can help identify program components that are working effectively and achieving desired outcomes. These strengths can be further developed and emphasized in future program design.
- Understanding the factors contributing to program success can help replicate and scale up effective interventions.
Identifying areas for improvement:
- Evaluation results can reveal program weaknesses or areas where desired outcomes are not being achieved. This information can be used to identify potential barriers or challenges that need to be addressed.
- By identifying specific areas for improvement, organizations can make targeted changes to program delivery, implementation, or resources allocation.
Implementing changes based on evaluation findings
Once the evaluation results have been analyzed and areas for improvement have been identified, it is important to implement changes to the program based on these findings.
Developing an action plan:
- Organizations should develop a clear and comprehensive action plan that outlines the specific changes that need to be made in response to the evaluation findings.
- The action plan should include specific objectives, timelines, responsible persons, and resources required to implement the changes.
Monitoring progress:
- It is important to monitor the progress of implementing the changes and regularly assess whether the desired improvements are being achieved.
- Data should be collected to measure the impact of the changes and determine if they are leading to program improvement.
Continuous learning and adaptation:
- Organizations should view evaluation as an ongoing process and continuously learn from their findings.
- By regularly evaluating and adapting program design based on evaluation results, organizations can improve program effectiveness and better meet the needs of their target beneficiaries.
Addressing Challenges in Program Evaluation
1. Lack of clarity in program goals and objectives
Lack of clarity in program goals and objectives can pose a major challenge in program evaluation. It is important for organizations to clearly define their goals and objectives before implementing a program. This requires a thorough understanding of the program’s purpose and desired outcomes. Without clear goals and objectives, it becomes difficult to measure the success or impact of a program.
2. Limited access to data
Limited access to data can hinder the effectiveness of program evaluation. Organizations may face challenges in collecting relevant data or accessing data from external sources. To address this challenge, organizations can establish data sharing agreements with partners or stakeholders, invest in data collection tools and technologies, or collaborate with research institutions or government agencies to access relevant data.
3. Insufficient resources
Insufficient resources, including financial, human, and time resources, can impact the quality and rigor of program evaluation. Organizations may face constraints in terms of budget, staff expertise, or time availability. To address this challenge, organizations can consider seeking funding or grants specifically for program evaluation, investing in training and capacity building for staff involved in evaluation, or prioritizing evaluation activities and allocating dedicated resources.
4. Resistance to evaluation
Resistance to evaluation can be a challenge in program evaluation, especially when there is a perception of evaluation as a critique or judgment of program performance. It is important for organizations to foster a culture of learning and improvement, where evaluation is seen as a valuable tool for enhancing program effectiveness. Engaging stakeholders and program participants in the evaluation process, and clearly communicating the purpose and benefits of evaluation, can help address resistance and promote a more positive attitude towards evaluation.
5. Complexity of program activities and outcomes
The complexity of program activities and outcomes can make evaluation challenging. Programs that have multiple components, target diverse populations, or aim to achieve long-term outcomes may require more sophisticated evaluation approaches. It is important for organizations to carefully design and plan their evaluation strategies, taking into account the complexity of their programs. This may involve using mixed methods approaches, engaging external evaluators with relevant expertise, or adapting evaluation methods to suit the specific context and needs of the program.
Building Evaluation Capacity in Civil Society Organizations
Program evaluation plays a crucial role in the success of civil society organizations. It helps these organizations assess the impact of their programs and make informed decisions about resource allocation. However, many civil society organizations lack the necessary evaluation capacity to effectively evaluate their programs.
One way to address this issue is by building evaluation capacity within these organizations. This involves equipping staff members with the knowledge and skills necessary to design and implement effective evaluations. Training workshops and educational resources can be provided to help staff members understand the principles of program evaluation and learn how to collect and analyze data.
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are also important components of building evaluation capacity. Civil society organizations can collaborate with each other to share best practices, lessons learned, and evaluation frameworks. This allows organizations to learn from each other’s experiences and make improvements in their own evaluation processes.
Engaging stakeholders
Engaging stakeholders in the evaluation process is another crucial aspect of building evaluation capacity. This involves involving key stakeholders, such as program beneficiaries, community leaders, and funders, in the evaluation planning and implementation. Their perspectives and feedback can provide valuable insights that help improve the relevance and effectiveness of the evaluation.
Creating a culture of evaluation
Finally, building evaluation capacity requires creating a culture of evaluation within civil society organizations. This involves fostering a mindset that values and prioritizes evaluation as a tool for learning and improvement. Leadership support, clear communication about the importance of evaluation, and integration of evaluation into the organization’s strategic planning processes can all contribute to creating a culture of evaluation.





