In today’s digital age, maintaining the right to privacy has become increasingly challenging. As individuals and organizations utilize technology to advance their objectives, the risk of intrusion on their privacy rises. This is especially pertinent for civil society organizations, which often deal with sensitive information related to their work on advocacy and activism. In order to protect civil society’s right to privacy, a robust legal framework is crucial.
The legal framework must begin with a strong recognition of the importance of privacy as a fundamental right. Privacy enables individuals and organizations to freely express themselves and engage in critical conversations without fear of surveillance or persecution. It provides the necessary space for civil society actors to operate independently, without undue interference from governments or other entities.
Furthermore, the legal framework should establish clear limitations on the actions that can be taken to invade privacy. It should require that any intrusion on privacy be justified by a legitimate purpose, such as national security or public interest, and be conducted in a manner that is proportional and necessary to achieve that purpose. These limitations would ensure that civil society actors are not unduly targeted or monitored without valid reason.
In addition, the legal framework should include safeguards to protect against unlawful surveillance and data breaches. This can be achieved through strong data protection laws that require organizations to implement appropriate security measures to safeguard the personal information they hold. It should also establish oversight mechanisms to ensure that any surveillance activities are subject to independent scrutiny and accountability.
Overall, the legal framework to protect civil society’s right to privacy should strike a balance between respecting the needs of individuals and organizations to operate freely, while also addressing legitimate concerns related to national security and public interest. It should provide clear guidelines and protections to prevent unauthorized intrusion and protect against unlawful surveillance. By doing so, it can ensure that civil society actors can continue to operate without fear of reprisal and contribute to the betterment of societies around the world.
Understanding the Importance of Privacy in Civil Society
Privacy is a fundamental human right that is essential for the functioning of a civil society. It allows individuals to have control over their personal information and protects them from unwarranted surveillance or intrusion. In the digital age, where information is easily accessible and shared, maintaining privacy becomes even more crucial.
Protection of privacy fosters trust and transparency in civil society. When individuals have confidence that their personal information is secure, they are more likely to engage in civic activities, share their opinions, and participate in public discourse. Privacy promotes open and honest communication, creating an environment where ideas can be freely expressed.
Privacy empowers individuals and promotes autonomy. It allows people to have control over their personal lives, make choices, and shape their identity without the fear of judgment or discrimination. This sense of autonomy is especially important for members of marginalized communities, as privacy can offer a shield against prejudice and oppression.
Privacy is essential for protecting sensitive information. In civil society, there are many organizations and individuals working on issues that require confidentiality, such as human rights activists, journalists, and whistleblowers. Privacy safeguards their work and allows them to investigate, report, and speak out without fear of reprisal.
Privacy plays a role in fostering innovation and creativity. When individuals feel that their ideas and creations are protected, they are more likely to take risks and explore new concepts. Privacy enables the free exchange of ideas, encourages collaboration, and supports the advancement of knowledge and progress in society.
Privacy is vital for maintaining a democratic society. It ensures that citizens can exercise their rights to freedom of speech, association, and assembly without fear of surveillance or persecution. Privacy protects the ability of civil society to challenge authority, hold those in power accountable, and advocate for social change.
In conclusion, privacy is a cornerstone of a thriving civil society. It promotes trust, empowers individuals, protects sensitive information, fosters innovation, and maintains democracy. Recognizing and upholding privacy rights is crucial to protect and preserve the values and principles that underpin civil society.
The Role of Privacy Laws in Safeguarding Civil Society
In today’s digital age, privacy laws play a crucial role in safeguarding the rights and security of civil society. Civil society organizations, such as non-governmental organizations and community-based groups, often handle sensitive information and engage in activities that require a certain level of privacy and protection.
Privacy laws provide the legal framework necessary to ensure that civil society’s right to privacy is respected and upheld. These laws establish guidelines for the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information, preventing unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive data. By establishing clear boundaries and obligations for both individuals and organizations, privacy laws create a safe environment for civil society to operate and communicate freely.
Protection against surveillance and intrusion
Privacy laws protect civil society from unwarranted surveillance and intrusion by both government and private entities. These laws regulate the use of surveillance technologies, such as wiretapping or electronic monitoring, ensuring that they are only used in accordance with legal processes and restrictions. By protecting civil society from unjustified surveillance and intrusion, privacy laws help to maintain the integrity and independence of these organizations.
Preserving freedom of speech and association
The right to privacy is closely linked to the freedom of speech and association, both fundamental pillars of civil society. Privacy laws help to preserve these rights by safeguarding the ability of individuals and organizations to express their opinions, gather, and associate freely without fear of reprisal or surveillance. By protecting the privacy of civil society actors, these laws ensure that they can operate without unwarranted interference and contribute to a vibrant democratic society.
In conclusion, privacy laws are essential in safeguarding civil society by protecting their right to privacy, ensuring protection against surveillance and intrusion, and preserving the freedom of speech and association. These laws create a legal framework that allows civil society organizations to operate freely, securely, and effectively, ultimately contributing to a healthy and democratic society.
Examining the Right to Privacy in International Conventions
The right to privacy is a fundamental human right recognized and protected by various international conventions and treaties. These international legal instruments acknowledge the importance of privacy in ensuring the dignity, autonomy, and freedom of individuals, and seek to safeguard it from unwarranted intrusion and surveillance.
One of the key international conventions that emphasizes the right to privacy is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1948. Article 12 of the UDHR explicitly recognizes that "no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy." This provision highlights the need for individuals to have control over their personal information and the freedom to choose when and how it is shared.
The right to privacy is also protected by the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), which was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1966. Article 17 of the ICCPR enshrines the right to privacy as follows: "No one shall be subjected to arbitrary or unlawful interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence." This provision emphasizes the importance of protecting not only individuals’ personal data but also their private spaces and communications.
In addition to these universal conventions, regional human rights frameworks also recognize and protect the right to privacy. For example, the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR), which was adopted by the Council of Europe in 1950, guarantees the right to respect for private and family life in Article 8. This provision has been interpreted by the European Court of Human Rights to encompass various aspects of privacy, including protection against surveillance and interception of communications.
Overall, international conventions and treaties play a crucial role in safeguarding the right to privacy. These legal frameworks establish the rights of individuals to privacy and provide a basis for holding governments accountable for any infringements on this fundamental right. It is essential for states to uphold their obligations under these conventions and ensure that civil society’s right to privacy is respected and protected.
The Impact of Technology on Civil Society’s Privacy
The rapid advancement of technology in recent years has had a profound impact on civil society‘s right to privacy. With the increasing use of internet-connected devices, social media platforms, and online communication tools, individuals are more vulnerable to privacy breaches than ever before.
One of the major concerns is the collection and storage of personal data by tech companies. Many popular platforms and applications collect vast amounts of data from their users, including their browsing history, location information, and even biometric data. This data can be used not only for targeted advertising but also for more nefarious purposes such as surveillance and profiling.
Another challenge posed by technology is the ease with which information can be shared and disseminated. With the click of a button, sensitive and private information can be exposed to a wide audience, often without the individual’s knowledge or consent. This has serious implications for civil society organizations, which rely on trust and confidentiality to carry out their work.
Furthermore, the rise of surveillance technologies such as facial recognition and data mining algorithms has raised concerns about the erosion of civil liberties. These technologies have the potential to track and monitor individuals’ activities, behaviors, and even thoughts, infringing on their right to privacy and freedom of expression.
In response to these challenges, there is a growing need for robust legal frameworks to protect civil society’s right to privacy. This includes clear regulations on data collection and storage, transparency in data practices, and enhanced safeguards against surveillance and intrusive technologies. Additionally, individuals must be equipped with the knowledge and tools to protect their own privacy, such as encryption and secure communication platforms.
Challenges Faced by Civil Society in Protecting Privacy
Civil society faces a number of challenges when it comes to protecting privacy in the legal framework. One of the main challenges is the lack of clear and comprehensive legislation addressing privacy rights. Many countries have existing laws that were drafted before the rise of the digital age, making it difficult to effectively protect privacy in the modern context. Civil society often has to navigate through a patchwork of outdated and inadequate laws, which can hinder their efforts to safeguard individuals’ privacy.
Another challenge is the increasing use of surveillance technologies by governments and other entities. Advances in technology have made it easier for governments to monitor and collect data on individuals, often without their knowledge or consent. Civil society organizations face an uphill battle in advocating for stronger privacy protections in the face of powerful surveillance capabilities. They must often rely on raising awareness and lobbying for legal reforms to address these privacy concerns.
Additionally, civil society has to contend with the growing phenomenon of data breaches and cyberattacks. These incidents can result in the exposure of personal information, leading to significant privacy breaches. Civil society organizations not only have to protect their own data, but also advocate for stronger safeguards and accountability measures to prevent data breaches and hold perpetrators accountable. This can be a daunting task, especially as cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated.
Furthermore, civil society often faces challenges in ensuring the privacy rights of marginalized and vulnerable groups. These groups may be disproportionately affected by privacy violations and may have limited access to legal resources to seek redress. Civil society organizations play a crucial role in advocating for the rights of these groups and ensuring that privacy protections extend to all individuals, regardless of their social or economic status. However, they may face resistance or opposition in their efforts, making it difficult to achieve meaningful change.
In conclusion, civil society faces various challenges in protecting privacy within the legal framework. From outdated legislation to surveillance technologies, data breaches, and marginalized groups, civil society has a complex task ahead. However, through advocacy, awareness-raising, and collaboration, civil society organizations continue to play a vital role in safeguarding privacy rights and upholding individuals’ right to privacy.
Exploring the Legal Tools to Protect Privacy in Civil Society
The Right to Privacy
The right to privacy is a fundamental human right that protects individuals from intrusion into their personal lives and allows them to control the collection, use, and disclosure of their personal information. In civil society, it is crucial to have robust legal tools in place to safeguard and protect privacy rights. Without such tools, individuals and organizations within civil society could be at risk of surveillance, harassment, and intimidation, which can have a chilling effect on their ability to freely express their views and engage in advocacy and activism.
Data Protection and Privacy Laws
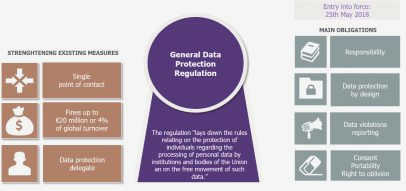
One legal tool that plays a vital role in protecting privacy in civil society is data protection and privacy laws. These laws aim to regulate the collection, storage, and processing of personal information by government and private entities. They provide individuals with certain rights, including the right to be informed about how their data is being used, the right to access their data, the right to rectify any inaccuracies, and the right to restrict or object to the processing of their data.
Strong data protection and privacy laws can give civil society organizations the confidence to collect and store personal information, such as membership details or contact information, knowing that they are legally obliged to handle this information responsibly and securely. These laws also provide individuals with avenues for seeking redress if their privacy rights are violated, such as the right to file complaints with data protection authorities or seek legal remedies through the courts.
Encryption and Secure Communication
Encryption and secure communication tools are another essential legal tool for protecting privacy in civil society. Encryption technology ensures that sensitive information, such as emails, chats, and files, is scrambled and unreadable to anyone who does not have the decryption key. This is particularly important for civil society organizations, as it enables them to communicate securely, protect the confidentiality of their work, and safeguard the personal information of their members and beneficiaries.
Furthermore, legal frameworks can promote the use of encryption by protecting the right to use encryption technologies and by prohibiting the forced disclosure of encryption keys or passwords. These measures are crucial in maintaining the integrity and privacy of civil society’s communications, as they prevent unauthorized access by governments or malicious actors.
International Human Rights Standards
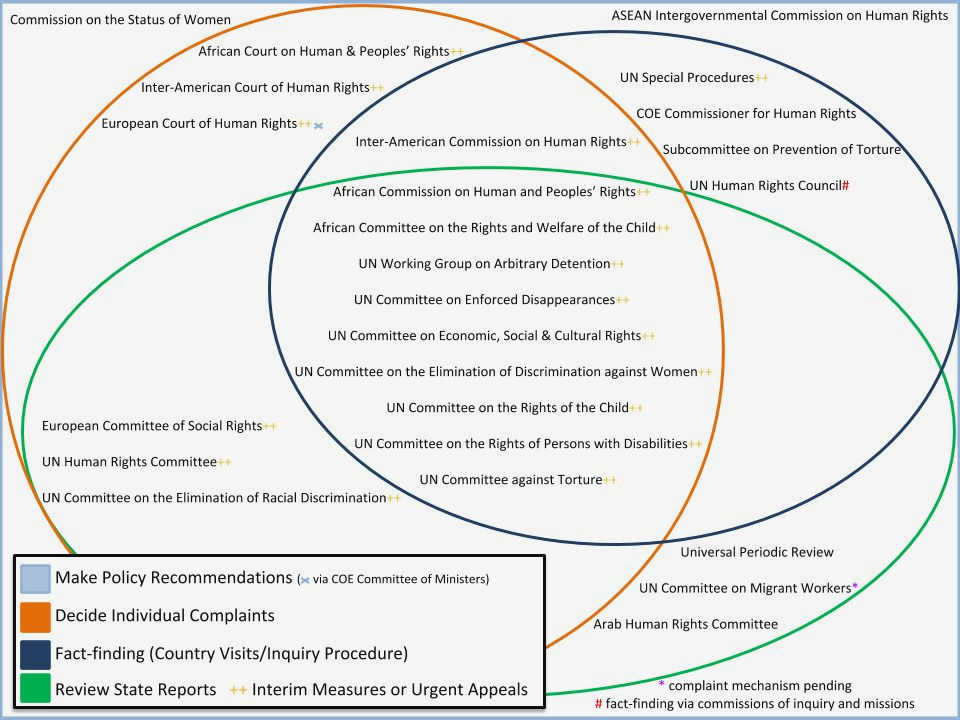
International human rights standards also play a significant role in protecting privacy in civil society. Treaties and conventions, such as the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR), recognize the right to privacy and set out the obligations of states in upholding this right. Civil society organizations can leverage these international human rights standards to advocate for stronger privacy protections and hold governments accountable for any violations.
Moreover, international mechanisms, such as the United Nations Human Rights Council and regional human rights courts, provide avenues for individuals and organizations to raise privacy concerns and seek remedies for violations. These mechanisms serve as important platforms for civil society to engage in dialogue and advocacy on privacy issues at the global or regional level.
The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations in Advocating for Privacy Rights
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in advocating for privacy rights in civil society. These organizations are independent and operate outside of government control, allowing them to work on behalf of individuals and communities to protect their right to privacy.
NGOs engage in various activities to promote and defend privacy rights. They conduct research to gather evidence and raise awareness about privacy issues, shining a light on the threats and violations faced by individuals and communities. Through their research findings, NGOs contribute to the development of legal frameworks and policies that protect privacy rights.
NGOs also engage in legal advocacy, using their expertise to challenge privacy-invasive practices and laws. They may file lawsuits, participate in legal proceedings, and provide legal representation to individuals whose privacy rights have been violated. By doing so, NGOs help establish legal precedents and standards that safeguard privacy.
In addition to research and legal advocacy, NGOs often collaborate with other civil society organizations, government agencies, and international bodies to advocate for privacy rights. They engage in public awareness campaigns, organizing workshops, seminars, and conferences to educate individuals about their privacy rights and provide them with tools and knowledge to protect themselves.
NGOs also engage in capacity-building activities, supporting individuals and communities in developing their digital literacy skills and understanding of privacy-related technologies. They may provide training, resources, and tools to help individuals navigate the complexities of the digital world while safeguarding their privacy.
Overall, NGOs play a critical role in advocating for privacy rights and ensuring that individuals and communities have the necessary protections in place. Their research, legal advocacy, collaboration, and capacity-building efforts contribute to the development of a robust legal framework and awareness around privacy issues, empowering individuals to exercise their right to privacy in an increasingly digital world.
Privacy Violations and Their Consequences for Civil Society
Privacy violations have far-reaching consequences for civil society, undermining the fundamental rights and freedoms that are necessary for a healthy democracy. When individuals’ privacy is violated, it erodes trust in institutions, stifles freedom of expression, and hampers the ability of civil society organizations to operate effectively.
One of the main consequences of privacy violations is the chilling effect it has on freedom of expression. When individuals feel that their privacy is not protected, they are less likely to speak out on important issues or engage in activism. This silencing effect is detrimental to civil society, as it prevents the free exchange of ideas and hampers the ability to mobilize for meaningful change.
Privacy violations also undermine trust in institutions, including government entities and civil society organizations. When individuals learn that their personal information has been collected, stored, or shared without their consent, it erodes their trust in those responsible. This distrust can have a cascading effect, as it may lead individuals to be less willing to engage with civil society organizations or seek help from government entities that are meant to protect their interests.
In addition to the immediate consequences of privacy violations, there can be long-term societal impacts. When individuals feel that their privacy is not adequately protected, they may be less likely to engage in activities that benefit society as a whole. For example, they may be less likely to participate in community initiatives, engage in political discourse, or share information that could be beneficial to others. This withdrawal from civic engagement can have a detrimental effect on the overall health of civil society.
To protect civil society and ensure the rights of individuals are respected, it is crucial to have a strong legal framework that safeguards privacy. This framework should include clear laws that restrict the collection and use of personal data, as well as robust enforcement mechanisms to hold violators accountable. Additionally, civil society organizations can play a role by advocating for privacy rights and educating individuals on how to protect their own privacy online.
Case Studies: Successful Efforts to Protect Civil Society’s Privacy
The Case of Sweden: Strengthening Legal Protections
In Sweden, there have been successful efforts to protect civil society‘s privacy through the implementation of strong legal frameworks. The Swedish government recognized the importance of safeguarding civil society organizations from unwarranted surveillance and interference, and enacted legislation that strictly regulates the collection, storage, and use of personal data. This has helped to ensure that civil society organizations can carry out their work without fear of surveillance or harassment.
The Case of Canada: Empowering Civil Society Through Encryption
In Canada, there has been a focus on empowering civil society to protect their privacy through the use of encryption technologies. The Canadian government, in partnership with civil society organizations, has provided resources and support to help these organizations implement robust encryption measures. This has enabled civil society organizations to securely communicate and transmit sensitive information without the risk of interception or unauthorized access.
The Case of Germany: Strengthening Data Protection Laws
Germany has taken significant steps to strengthen data protection laws and ensure the privacy rights of civil society organizations are upheld. The German government has implemented comprehensive legislation that mandates strict data protection measures, including the appointment of data protection officers within civil society organizations. This has helped to create a culture of privacy awareness and compliance, ensuring that civil society organizations can operate with confidence and without the fear of privacy violations.
The Case of South Africa: Challenging Surveillance Policies
In South Africa, civil society organizations have successfully challenged surveillance policies that were infringing on their privacy rights. Through strategic litigation and advocacy efforts, these organizations were able to raise awareness about the impact of surveillance on civil society and demonstrate the need for stronger protections. As a result, the South African government reviewed and revised its surveillance policies to align with international human rights standards, providing greater protection for civil society’s right to privacy.
In conclusion, these case studies demonstrate the various successful efforts that have been made to protect civil society’s privacy. Whether through strengthening legal protections, empowering civil society through encryption, or challenging unjust surveillance policies, these initiatives have helped to safeguard the privacy of civil society organizations and enable them to continue their important work without interference or harassment.
Recommendations for Strengthening Privacy Protection in Civil Society
Educate and Empower Civil Society Organizations
To enhance privacy protection in civil society, it is crucial to educate and empower organizations to understand the importance of privacy and the potential risks they face. This can be achieved through workshops, training programs, and awareness campaigns that focus on the legal and technical aspects of privacy protection. Organizations should be equipped with knowledge and tools to assess their privacy needs, develop privacy policies, and implement appropriate security measures.
Establish Clear Privacy Policies
Civil society organizations should establish clear and comprehensive privacy policies that outline the type of personal data collected, how it is used, who has access to it, and how long it is retained. These policies should be easily accessible to users and provide transparent information about the organization’s data handling practices. Regular reviews and updates to privacy policies are also essential to ensure compliance with evolving legal and technological developments.
Implement Strong Data Security Measures
Effective privacy protection requires the implementation of strong data security measures by civil society organizations. This includes encryption of sensitive data, regular data backups, access controls, and robust security protocols. Organizations should also conduct regular security audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly. By adopting best practices in data security, organizations can better protect the privacy of individuals and mitigate the risk of data breaches.
Advocate for Strong Privacy Laws and Regulations
Civil society organizations play a vital role in advocating for strong privacy laws and regulations that protect the rights of individuals. They should actively engage in policy debates, contribute to the development of privacy legislation, and collaborate with government agencies and other stakeholders to secure comprehensive privacy protection. By advocating for privacy at the legal and regulatory level, civil society organizations can help create an enabling environment that upholds the privacy rights of all individuals.
Collaborate on Privacy Protection Initiatives
Collaboration among civil society organizations is essential for strengthening privacy protection. Organizations should come together to share best practices, exchange insights, and collectively address common challenges. This can be achieved through partnerships, networks, and forums dedicated to privacy protection. By working together, civil society organizations can pool their expertise and resources to develop innovative solutions and collectively promote a culture of privacy in the society.
- Conclusion: Strengthening privacy protection in civil society requires a multi-faceted approach that involves education, clear policies, robust security measures, advocacy, and collaboration. By implementing these recommendations, civil society organizations can enhance their privacy practices and safeguard the rights of individuals.






