In recent years, there has been an increasing recognition of the urgent need to address climate change. Governments, corporations, and international organizations have all played a role in shaping climate change legislation, but another important factor has emerged as a significant force for change: grassroots movements and civil society activism.
Civil society activism has proven to be a powerful tool in shaping climate change legislation because it represents the voice and concerns of ordinary citizens. These grassroots movements, often comprised of local communities, NGOs, and individuals, play a crucial role in raising awareness about the realities of climate change and advocating for policy changes that prioritize sustainability and environmental preservation.
One of the key ways in which grassroots movements shape climate change legislation is through their ability to mobilize public support. By organizing protests, rallies, and campaigns, these activists are able to bring attention to the urgent need for action on climate change. Through their efforts, they are able to capture the attention of policymakers and push for legislative changes that align with their goals and demands.
Furthermore, grassroots movements often engage in direct advocacy and lobbying activities to push for specific changes in climate change legislation. They may meet with lawmakers, submit written proposals, or engage in public consultations to ensure that their concerns and recommendations are taken into account. By working directly with policymakers, these activists are able to shape the narrative around climate change and influence the development of legislation that reflects the needs and priorities of the communities they represent.
In conclusion, grassroots movements and civil society activism have a significant impact on climate change legislation. By mobilizing public support, engaging in direct advocacy, and raising awareness about the urgency of the issue, these activists are able to shape the policies and strategies that will determine the future of our planet. The power of ordinary citizens should not be underestimated, as they have the ability to drive meaningful change and ensure that climate change remains at the top of the global agenda.
Overview of Climate Change Legislation
Climate change legislation refers to laws and regulations enacted by governments to address the challenges posed by climate change. These laws aim to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy sources, and adapt to the impacts of climate change. Climate change legislation plays a crucial role in shaping national and international efforts to combat climate change and transition to a low-carbon economy.
Countries around the world have implemented various climate change legislation mechanisms, including targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, supporting renewable energy development, and promoting energy efficiency measures. These legislations are often guided by international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which sets global goals for limiting global warming and promoting sustainable development.
Mitigation Measures
Climate change legislation includes measures aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change. These measures often include setting emission reduction targets, implementing cap-and-trade systems, promoting renewable energy sources, and supporting energy efficiency measures. Additionally, climate change legislation may incentivize the adoption of clean technologies and the development of low-carbon industries.
Adaptation Strategies
In addition to mitigation measures, climate change legislation also focuses on adaptation strategies. These strategies aim to help societies and ecosystems adapt to the changes already occurring and those expected in the future. They often involve implementing measures to enhance resilience, protect vulnerable communities and ecosystems, and integrate climate change considerations into urban planning and infrastructure development.

International Cooperation
Climate change legislation is not limited to national efforts but also involves international cooperation. Countries work together through international agreements and organizations to address global climate challenges. These agreements aim to coordinate efforts, share knowledge and resources, and provide support to developing countries in their climate actions. International climate change legislation is crucial for achieving global climate goals and ensuring a coordinated and effective response to climate change.
Monitoring and Enforcement
To ensure the effectiveness of climate change legislation, monitoring, and enforcement mechanisms are crucial. These mechanisms involve monitoring countries’ progress in achieving their climate goals, tracking the implementation of climate policies and measures, and assessing the impacts of these measures. Additionally, enforcement mechanisms may include penalties for non-compliance and accountability mechanisms to hold governments and other actors responsible for their climate actions.
In conclusion, climate change legislation encompasses a wide range of measures aimed at addressing climate change challenges. It includes both mitigation and adaptation strategies, international cooperation, and monitoring and enforcement mechanisms. Climate change legislation is crucial for driving the transition to a low-carbon economy and ensuring a sustainable future for all.
Importance of Grassroots Movements
Grassroots movements play a crucial role in shaping climate change legislation and driving meaningful change in communities and societies. These movements, driven by passionate individuals and organizations, have the power to mobilize communities, raise awareness, and advocate for policy changes that address the urgent need for climate action.
Empowerment: Grassroots movements empower individuals to take action and have a voice in shaping climate policies. By organizing and mobilizing at the local level, these movements provide a platform for individuals to express their concerns, share their experiences, and collectively work towards a sustainable future.
Local Solutions: Grassroots movements are often rooted in communities, and as such, they are uniquely positioned to address the specific climate challenges and opportunities faced by those communities. They can develop and promote local solutions that are tailored to the needs and priorities of the people who are directly affected by climate change.
Awareness and Education: Grassroots movements play a crucial role in raising awareness about the impacts of climate change and educating communities about sustainable practices. By organizing events, workshops, and campaigns, they can engage individuals and help them understand the importance of taking action to mitigate and adapt to climate change.

Driving Policy Change: Grassroots movements have the power to influence policy-making processes and shape climate change legislation. Through grassroots mobilization, advocacy, and lobbying efforts, these movements can put pressure on policymakers to prioritize climate action and develop policies that support sustainable practices and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Building Momentum: Grassroots movements act as catalysts for change by building momentum and driving a collective sense of urgency in addressing climate change. They inspire and motivate individuals to join the movement, creating a ripple effect that can lead to more widespread action and a stronger voice for climate justice.
In conclusion, grassroots movements are instrumental in shaping climate change legislation and driving meaningful change. By empowering individuals, promoting local solutions, raising awareness, driving policy change, and building momentum, these movements are essential in addressing the urgent need for climate action at both the local and global levels.

Role of Civil Society Activism
Civil society activism plays a crucial role in shaping climate change legislation. Through their grassroots efforts, activists raise awareness about the urgency of climate change and mobilize support for policy change.
Raising Awareness
Civil society activists play a crucial role in raising awareness about the impacts of climate change on communities and the environment. They organize educational campaigns, public events, and media campaigns to inform the public about the scientific consensus on climate change and advocate for immediate action.
Mobilizing Support
One of the key contributions of civil society activism is its ability to mobilize support for climate change legislation. Activists utilize various strategies such as lobbying, public demonstrations, and online activism to engage and empower the public and policymakers. By organizing protests, rallies, and petitions, they apply pressure on policymakers to prioritize climate change solutions.
Influencing Policy
Civil society activists have successfully influenced climate change legislation by bringing their concerns and demands to the attention of policymakers. Through their collective action, they have pushed for the adoption of renewable energy policies, stricter emission standards, and the implementation of climate change adaptation measures. They also provide input and expertise during policy development processes, ensuring that the interests of communities and the environment are considered.
Driving Solutions
Civil society activism goes beyond advocacy and awareness-raising. Activists also drive solutions by promoting sustainable practices, innovation, and community-led initiatives. They develop and implement projects that demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture. Their initiatives inspire individuals, communities, and businesses to take action on climate change.
Conclusion
The role of civil society activism in shaping climate change legislation cannot be underestimated. Through their grassroots efforts, activists raise awareness, mobilize support, influence policy, and drive solutions. Their collective action is essential in addressing the global challenge of climate change and creating a sustainable future for all.
Case Studies: Successful Grassroots Campaigns
The Sunrise Movement
The Sunrise Movement is a youth-led organization advocating for policies to address climate change and create millions of green jobs. The movement gained national attention in the United States in 2018 when they staged sit-ins at the offices of Democratic lawmakers, demanding they support the Green New Deal. The Sunrise Movement used social media to mobilize and engage young people, organizing rallies, town hall meetings, and lobbying efforts. Their grassroots campaign was successful in pushing the Green New Deal onto the political agenda and gaining support from influential politicians.
350.org
350.org is a global grassroots movement working to solve the climate crisis. The organization was founded in 2008 by a group of environmental activists, including writer and activist Bill McKibben. 350.org focuses on grassroots organizing, using online platforms and local campaigns to mobilize communities around the world. One of their successful campaigns was the Global Divestment Movement, which urged institutions to divest from fossil fuels. The movement gained traction globally, with universities, cities, and financial institutions committing to divest from fossil fuels, putting pressure on the fossil fuel industry and raising public awareness about the climate crisis.
Extinction Rebellion
Extinction Rebellion is a global environmental movement that uses civil disobedience and non-violent protest to demand urgent action on climate change. The movement was founded in the United Kingdom in 2018 and has since spread to many countries. Extinction Rebellion’s successful grassroots campaign was highlighted during their April Rebellion in 2019, where thousands of activists occupied major landmarks in London and engaged in acts of civil disobedience to draw attention to the climate emergency. The campaign led to widespread media coverage and forced the government to declare a climate emergency, signaling a significant shift in political discourse around climate change.
Greenpeace’s Save the Arctic
Greenpeace’s Save the Arctic campaign was launched in 2012, with the aim of protecting the Arctic region from oil drilling and the effects of climate change. The campaign mobilized millions of supporters worldwide through online platforms, petitions, and direct actions. Greenpeace organized protests, occupied oil rig platforms, and used creative tactics to draw attention to the destruction of the Arctic ecosystem. The campaign successfully influenced public opinion and forced major companies to abandon drilling in the Arctic, highlighting the power of grassroots activism in shaping climate change legislation.
In conclusion, these case studies demonstrate the power of grassroots movements in shaping climate change legislation. Through strategic organizing, mobilization of supporters, and creative tactics, these campaigns were able to bring attention to the urgency of the climate crisis and push for transformative policy changes. Grassroots activism plays a crucial role in holding governments and corporations accountable and driving the transition to a more sustainable and equitable society.
Influence of Public Opinion
Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping climate change legislation. The level of public awareness and concern regarding climate change can have a significant impact on the political will to take action. When a grassroots movement successfully raises public awareness and mobilizes support, it can create a strong public demand for climate change legislation.
Public support: Grassroots movements can generate widespread public support for climate change legislation by effectively communicating the urgency and importance of addressing the issue. Through rallies, protests, and social media campaigns, these movements can reach a large audience and mobilize public opinion in favor of stronger climate change policies.
Political pressure: Public opinion can also exert pressure on politicians to prioritize climate change legislation. When faced with a vocal and active constituency, politicians are more likely to respond to the demands of the public and take action on climate change.
Election impact: The influence of public opinion is further amplified during elections. Politicians often take into account the views and concerns of their constituents when formulating their campaign platforms. If climate change is a top concern for voters, candidates may be more inclined to make climate change legislation a central part of their platform.
Critical mass: Public opinion can be particularly powerful when it reaches a critical mass. When a significant portion of the population becomes concerned about climate change and demands action, it becomes increasingly difficult for politicians to ignore their voices. This can lead to a shift in the political landscape, with more politicians advocating for and implementing climate change policies.
Role of media: The media also plays a crucial role in influencing public opinion on climate change. Through thorough and accurate reporting, journalists can educate the public about the science and impacts of climate change, and highlight the efforts of grassroots movements. This can further amplify public support for climate change legislation.
Collaboration with Political Leaders
Building alliances for change
In order to effectively shape climate change legislation, grassroots movements often seek collaboration with political leaders. This collaboration involves building alliances and relationships with officials who have the power to enact meaningful policy changes. By working together with politicians, activists can amplify their voices and push for their demands to be incorporated into policy decisions.
Leveraging political connections
Grassroots movements understand the importance of leveraging political connections to achieve their goals. They actively engage with politicians who are sympathetic to their cause, utilizing their networks and relationships to advocate for climate change legislation. By forging alliances with key decision-makers, activists can access channels of influence that may not be available to them otherwise.
Education and awareness campaigns
Collaboration with political leaders also involves organizing education and awareness campaigns to highlight the urgency and importance of climate change action. Grassroots movements work with politicians to host public forums, town hall meetings, and informational sessions that focus on informing the public and policymakers about the need for effective climate change legislation. These campaigns aim to mobilize public support and create a sense of collective responsibility for addressing climate change.
Policy proposals and advocacy
Grassroots movements collaborate with political leaders by developing and presenting policy proposals that address climate change issues. These proposals are based on extensive research and are presented to politicians as evidence-based solutions that can be implemented to mitigate the effects of climate change. By engaging in policy discussions and advocacy, activists seek to influence the decision-making process and ensure that the voice of civil society is heard.
Monitoring and accountability
Collaboration with political leaders also involves monitoring and holding them accountable for their actions. Grassroots movements maintain a watchful eye on politicians to ensure that they follow through on their promises and commitments regarding climate change legislation. They organize monitoring campaigns, audits, and public reports to assess the progress made by political leaders and to keep the public informed about their performance on climate change issues.
Working towards long-lasting change
Through collaboration with political leaders, grassroots movements aim to foster long-lasting change in climate change legislation. By forming alliances and actively engaging with politicians, activists can push for more ambitious policies and regulations that address the root causes of climate change. This collaborative approach recognizes the importance of both grassroots activism and political leadership in shaping effective climate change legislation.
Challenges and Obstacles
Funding limitations
One of the primary challenges facing grassroots movements in shaping climate change legislation is the lack of sufficient funding. Activists often rely on donations and grants from individuals and organizations, which may not always be consistent or adequate. The limited financial resources restrict their ability to organize campaigns, conduct research, and advocate for policy changes effectively.
Resistance from powerful stakeholders
Grassroots movements advocating for climate change legislation often face resistance from powerful stakeholders, such as corporations and industry groups. These stakeholders have a vested interest in maintaining the status quo and may employ their influence and resources to block or undermine efforts for meaningful change. Overcoming such resistance requires significant mobilization of public support, strategic alliances, and skillful lobbying.
Lack of political will
Another obstacle faced by grassroots movements is the lack of political will among decision-makers to prioritize climate change legislation. Politicians may be more focused on short-term gains or may be influenced by powerful lobbies that oppose stringent environmental regulations. Building pressure and awareness among the general public is crucial in order to push politicians to take necessary action and prioritize climate change on their agendas.
Complexity of the legislative process
The legislative process for climate change policies can be complex and lengthy, making it difficult for grassroots movements to navigate and influence. Understanding the intricate workings of legislation, building alliances with sympathetic lawmakers, and having a comprehensive understanding of the political landscape are essential for effective grassroots advocacy. Additionally, the need to adapt to changing political dynamics and maintain momentum for change adds further complexity to the process.
Coordination and collaboration
For grassroots movements to have a meaningful impact, it is crucial for them to coordinate and collaborate with other organizations and individuals who share similar goals. However, achieving effective coordination and collaboration can be challenging due to diverse interests and priorities among different stakeholders. Overcoming these challenges requires building strong networks, maintaining open lines of communication, and finding common ground to work towards shared objectives.
In conclusion, grassroots movements dedicated to shaping climate change legislation face various challenges and obstacles. These include funding limitations, resistance from powerful stakeholders, lack of political will, the complexity of the legislative process, and the need for coordination and collaboration. Overcoming these obstacles requires strategic planning, alliances, public support, and persistent advocacy efforts.
Global Impact of Grassroots Movements
Grassroots movements have a significant global impact on addressing and shaping climate change legislation. These movements, driven by civil society activism, play a vital role in amplifying the voices and concerns of communities affected by climate change.
Engagement and Awareness: Grassroots movements raise awareness about climate change at the local, national, and international levels. Through protests, marches, and public campaigns, they bring attention to the urgency of taking action to mitigate the effects of climate change. By engaging communities and mobilizing support, grassroots movements create a sense of collective responsibility and encourage individuals to make sustainable choices in their daily lives.
Policy Influence: Grassroots movements can have a direct impact on climate change legislation. Through lobbying, advocacy, and grassroots organizing, they pressure governments to adopt and implement comprehensive policies to address climate change. Many successful environmental policies, such as carbon pricing and renewable energy standards, have been influenced by grassroots movements. These movements also hold policymakers accountable for fulfilling their commitments and taking bold actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
International Cooperation: Grassroots movements contribute to the global conversation on climate change by fostering international cooperation and collaboration. They facilitate knowledge sharing and the exchange of best practices among activists, organizations, and governments from different countries. Grassroots movements also participate in international conferences and negotiations, representing the interests of affected communities and advocating for ambitious climate targets.
Empowerment and Justice: Grassroots movements empower marginalized communities and amplify their voices in climate change discussions. They challenge the disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations and advocate for climate justice. Grassroots movements promote inclusivity in decision-making processes and push for policies that address the needs and concerns of the most affected communities, ensuring a just transition to a sustainable future.
In conclusion, grassroots movements have a global impact on climate change legislation by raising awareness, influencing policies, fostering international cooperation, and advocating for justice. These movements are essential in driving the necessary actions needed to combat climate change and ensure a sustainable future for all.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Educate and engage the public
One of the key lessons learned from grassroots movements shaping climate change legislation is the importance of educating and engaging the public. Successful movements have found ways to effectively communicate the urgency and importance of climate action to a wide range of audiences, from policymakers to everyday citizens. By providing clear and accessible information about the scientific consensus on climate change, the potential impacts of inaction, and the benefits of taking action, activists can galvanize public support and build momentum for policy change.
Build diverse coalitions
Grassroots movements have also learned the value of building diverse coalitions. By partnering with a wide range of organizations, including environmental groups, social justice advocates, labor unions, and faith-based organizations, activists can amplify their message and increase their reach. This collaborative approach not only brings together different perspectives and expertise, but also increases the likelihood of success by widening the base of support and building a stronger movement.
Use a variety of tactics
Effective grassroots movements have found that using a variety of tactics can be more impactful than relying on a single approach. While protests and demonstrations can help raise awareness and put pressure on policymakers, they should be complemented by other strategies such as lobbying, grassroots organizing, media campaigns, and legal challenges. This multi-pronged approach ensures that activists are reaching different audiences, exerting pressure on multiple fronts, and maximizing their chances of success.
Be resilient and adaptable
One of the most important lessons learned from grassroots movements shaping climate change legislation is the need for resilience and adaptability. Change takes time, and setbacks and obstacles are inevitable. Activists must be prepared for long-term engagement, celebrate small victories along the way, and persist in the face of challenges. They should also be willing to adapt their strategies and tactics as circumstances change, and learn from both their successes and failures in order to continuously improve their approach.
Collaborate with policymakers
Lastly, successful grassroots movements understand the importance of collaborating with policymakers. While activism can help push for change from outside the system, it is equally important to work with policymakers who are supportive of climate action and share similar goals. By building relationships, providing expert input, and participating in the policy-making process, activists can shape legislation and ensure that it aligns with their vision for a sustainable future.

In conclusion, grassroots movements have made significant contributions to shaping climate change legislation by employing various strategies and tactics. The lessons learned from these movements highlight the importance of educating and engaging the public, building diverse coalitions, using a variety of tactics, being resilient and adaptable, and collaborating with policymakers. By applying these best practices, activists can amplify their impact and create meaningful change in addressing the urgent challenge of climate change.
Future Outlook: Mobilizing for Change
The future outlook for mobilizing for change in climate change legislation is promising. As grassroots movements continue to gain momentum and public awareness about the urgency of addressing climate change grows, there is a greater potential for significant policy shifts. Civil society activism has proven to be a powerful force in shaping climate change legislation, and its impact is expected to continue growing in the future.
Collaborative efforts: Moving forward, it is essential to foster collaboration among various civil society groups, including environmental organizations, community activists, and indigenous peoples. By combining their efforts and advocating for common goals, these groups can amplify their collective voices and create a united front for change. Collaborative efforts can also help bridge gaps between different perspectives and ensure that marginalized voices are heard and included in policy-making processes.
Global engagement: Mobilizing for change requires global engagement, as climate change is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Grassroots movements should aim to establish connections and partnerships with like-minded organizations and activists around the world. By working together on a global scale, these movements can exert pressure on governments and advocate for comprehensive climate change policies.
Youth activism: The involvement of young people is crucial for mobilizing for change. Youth activists have been at the forefront of climate change movements, demanding action from governments and corporations. Their energy, passion, and fresh perspectives bring new ideas and solutions to the table. Encouraging and supporting youth activism can help drive the momentum for change and ensure that future generations inherit a sustainable planet.
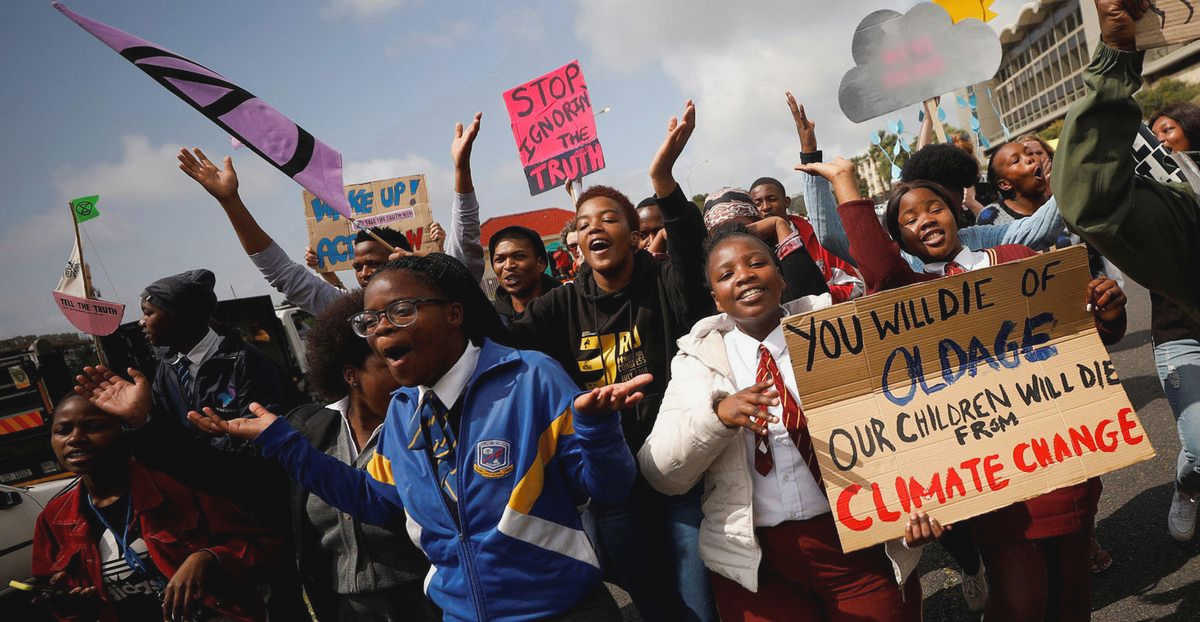
Policy advocacy: Mobilizing for change also involves strategic policy advocacy. Civil society groups should actively engage with policymakers, providing them with evidence-based research, expert opinions, and grassroots perspectives. By building relationships with key decision-makers and influencing the policy-making process, these groups can effectively shape climate change legislation and ensure that it aligns with the demands of the public.
Educating and raising awareness: Mobilizing for change requires continuous education and raising awareness about the impacts of climate change and the urgency of taking action. Civil society groups can play a crucial role in educating the public through campaigns, workshops, and community outreach programs. By empowering individuals with knowledge and encouraging a shift in behavior, these groups can generate broader public support for climate change legislation and create a sense of urgency for action.
In conclusion, the future outlook for mobilizing for change in climate change legislation is hopeful. Through collaborative efforts, global engagement, youth activism, policy advocacy, and education, civil society activism can continue to shape climate change legislation and drive meaningful change for a sustainable future.





