As civil society organizations continue to play a vital role in addressing social issues and driving positive change, the need for effective measurement of their impact has become increasingly important. Measuring social impact provides insights into the effectiveness of these organizations and helps them make informed decisions about resource allocation and programmatic strategies.
One key indicator of success for civil society organizations is the ability to demonstrate tangible results through measurable outcomes. By tracking and evaluating the impact of their programs and initiatives, organizations can showcase the value of their work to stakeholders, funders, and the communities they serve.
Creating a framework for measuring social impact involves identifying relevant metrics and indicators that align with the organization’s mission and goals. These metrics can include both qualitative and quantitative data, such as surveys, interviews, and financial reports, to provide a comprehensive view of the impact being made.
Furthermore, the process of measuring social impact not only helps organizations assess their own effectiveness but also fosters accountability and transparency. By regularly reporting on their achievements and challenges, civil society organizations can build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to achieving meaningful and sustainable change.
Why Measuring Social Impact Matters
Measuring social impact is crucial for civil society organizations as it enables them to assess the effectiveness of their programs and initiatives. By quantifying the outcomes and changes brought about by their work, organizations can gain valuable insights into whether they are achieving their intended goals and making a positive difference in people’s lives. Without measuring social impact, it becomes difficult to determine the real value and value for money of the organization’s efforts.
Transparency and Accountability: Measuring social impact helps ensure transparency and accountability within civil society organizations. By evaluating and reporting on their impact, organizations demonstrate their commitment to achieving their social mission and build trust among stakeholders, including funders, donors, and the public. It allows them to show that they are using resources efficiently and effectively, thus enhancing their credibility and reputation.
Evidence-based Decision Making: Measuring social impact provides civil society organizations with evidence to support decision making. It allows them to identify what works and what doesn’t, enabling them to allocate resources effectively and prioritize areas that yield the greatest impact. By collecting and analyzing data on outcomes and changes, organizations can make informed decisions that lead to better program design, implementation, and evaluation.
Learning and Improvement: Measuring social impact facilitates learning and improvement within civil society organizations. It enables them to identify successes and failures, understand the factors that contribute to positive outcomes, and learn from best practices. By continuously monitoring and evaluating their impact, organizations can adapt and improve their strategies to better address the needs and challenges of the communities they serve, ultimately increasing their overall effectiveness.
Advocacy and Policy Influence: Measuring social impact provides civil society organizations with data that can be used for advocacy and policy influence. When organizations are able to demonstrate the positive changes they are making in society, they can leverage this information to advocate for policy changes, attract additional funding, and influence decision-makers to prioritize issues that align with their mission. Measuring social impact gives organizations a powerful tool to make a compelling case for the importance of their work.

The Value of Accountability
Accountability is a fundamental aspect of measuring social impact in civil society. It refers to the responsibility to be transparent and answerable for one’s actions and decisions. The value of accountability lies in its ability to ensure that organizations and individuals are held to high standards of performance and ethical conduct.
Transparency
One of the key components of accountability is transparency. Through transparency, organizations and individuals are able to provide clear and open information about their activities, decision-making processes, and outcomes. Transparency fosters trust and credibility among stakeholders, as it allows them to understand how resources are being utilized and the impact that is being achieved.
Ethical Conduct
Accountability also encompasses ethical conduct. It requires organizations and individuals to adhere to a set of ethical principles and values in their actions and decision-making. Ethical conduct ensures that the social impact being measured is achieved in a manner that respects human rights, promotes fairness and equality, and is aligned with the overall objectives of civil society.
Performance Improvement
Accountability plays a crucial role in driving performance improvement. By setting clear expectations and holding individuals and organizations accountable for their actions, it creates a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Through accountability, civil society organizations are able to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement, allowing them to enhance their effectiveness and maximize their social impact.
In conclusion, accountability is a vital element in measuring social impact within civil society. It promotes transparency, ethical conduct, and performance improvement, enabling organizations and individuals to ensure that their actions and decisions are contributing to positive and meaningful change. By embracing accountability, civil society can enhance its success and effectiveness in addressing social issues and creating a better future for all.
The Role of Key Indicators
The role of key indicators in measuring social impact cannot be overstated. These indicators provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and success of civil society initiatives. They allow organizations to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of their work.
Key indicators act as a roadmap for organizations, guiding them towards their goals and helping them stay on track. By setting clear and measurable indicators, organizations can assess their progress and make data-driven decisions. These indicators can be used to monitor the implementation of programs or projects, measure outcomes and impact, and evaluate the overall effectiveness of interventions.
Key indicators also facilitate transparency and accountability in the civil society sector. By publicly reporting on these indicators, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to achieving social impact and can be held accountable to stakeholders, funders, and the general public. This not only builds trust and credibility, but also allows for greater collaboration and learning among organizations.
Furthermore, key indicators can inform resource allocation and help organizations prioritize their efforts. By analyzing data and trends, organizations can identify which interventions are most effective and efficient, and allocate their limited resources accordingly. This ensures that resources are used in the most impactful and sustainable way, maximizing social return on investment.
In summary, key indicators play a crucial role in measuring social impact by providing organizations with a roadmap, promoting transparency and accountability, and informing resource allocation. By effectively using key indicators, civil society organizations can drive positive change and make a lasting impact on society.
Measuring Civil Society Success
Civil society organizations play a crucial role in promoting social change and addressing societal issues. They often tackle challenges such as poverty, inequality, human rights violations, and environmental degradation. However, evaluating the success and impact of these organizations can be complex.
Defining and measuring success
To measure the success of civil society organizations, it is important to first define what success means in the context of their work. Success can vary depending on the organization’s objectives and the specific issues they are addressing. It may involve achieving policy changes, empowering marginalized communities, or raising awareness about a particular cause. Defining the desired outcomes is crucial for measuring success.
Key indicators for measuring impact
When measuring the success of civil society organizations, it is important to identify key indicators that reflect the organization’s impact. These indicators can include quantitative data, such as the number of people reached or the amount of funds raised. Additionally, qualitative data, such as personal stories or testimonies, can provide valuable insights into the impact of the organization’s work.

Furthermore, indicators should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure that the measurement process is effective and meaningful. This requires setting clear targets and regularly monitoring progress towards those targets.
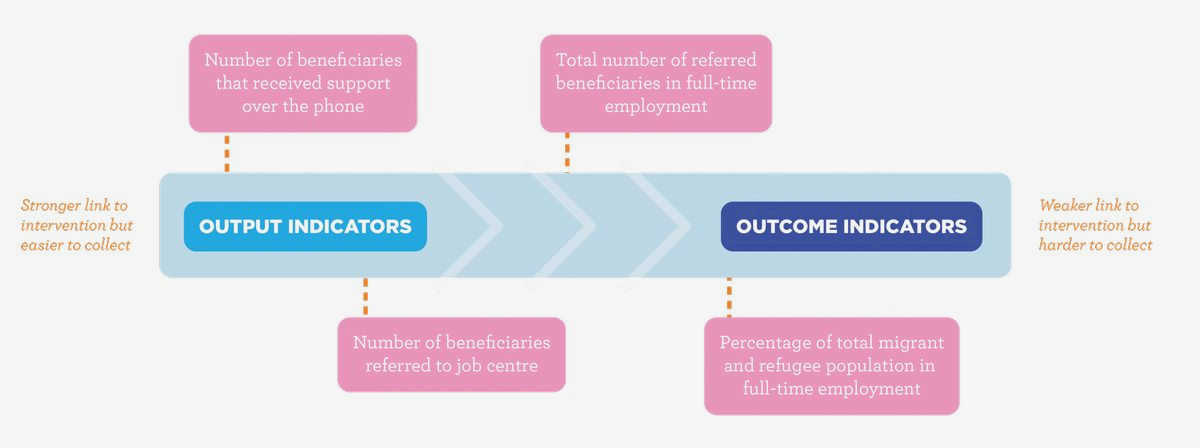
The role of evaluation frameworks
Evaluation frameworks can help civil society organizations assess their success and social impact more systematically. These frameworks provide a structured approach for evaluating the organization’s activities, outcomes, and overall effectiveness.
One common evaluation framework is the Theory of Change, which helps organizations articulate their intended impact and how they plan to achieve it. By mapping out the causal pathway between activities and outcomes, civil society organizations can better understand and measure their success.
The importance of learning and improvement
Measuring civil society success is not just about collecting data and numbers; it is also about learning from the findings and using them to improve future interventions. Organizations should regularly reflect on their results and use them to inform their strategies and decision-making.
Sharing findings and lessons learned with other organizations and stakeholders can also contribute to collective learning and drive broader social change. Collaboration and knowledge-sharing among civil society organizations can help amplify their impact and increase the effectiveness of their interventions.
In conclusion, measuring civil society success is crucial for ensuring accountability, learning, and overall effectiveness. By defining success, identifying key indicators, and using evaluation frameworks, civil society organizations can better understand their impact and continuously improve their work.
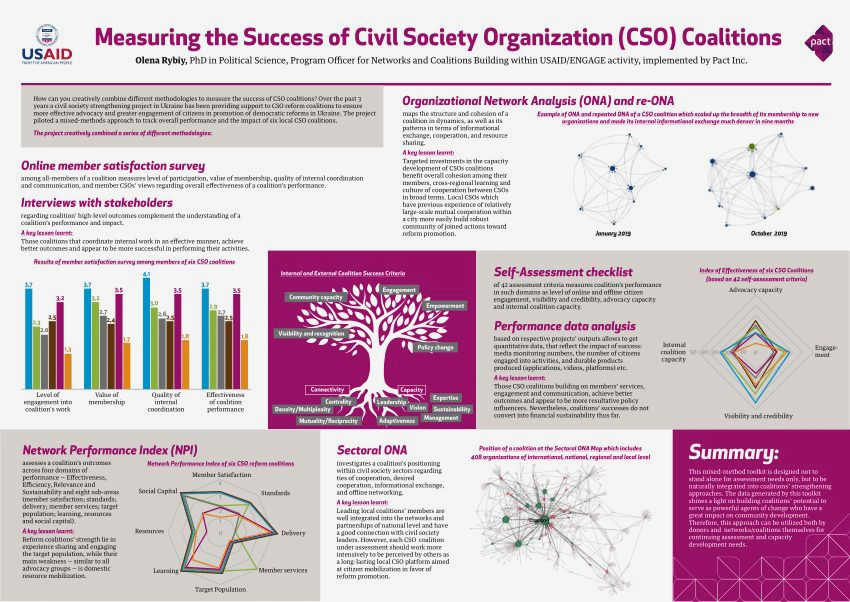
The Challenge of Quantifying Impact
Measuring social impact is a complex and challenging task for civil society organizations. While the ultimate goal of these organizations is to bring about positive change in society, quantifying the impact of their actions is not always straightforward.
One of the main challenges in quantifying impact is the lack of standardization in measurement methods. Different organizations may use different approaches and indicators to assess their impact, making it difficult to compare and analyze their results. This lack of standardization also makes it challenging for funders and stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of these organizations.
Moreover, the nature of social impact itself poses inherent challenges. Unlike financial or economic indicators, social impact is often intangible and difficult to quantify. It involves measuring changes in attitudes, behaviors, and social outcomes, which can be subjective and context-dependent.
Another challenge is the long-term nature of social impact. Many social problems are complex and multifaceted, requiring sustained efforts over time to achieve meaningful change. However, measuring and attributing impact to specific interventions can be difficult, as there are often multiple factors and actors involved in bringing about social change.
Despite these challenges, there is a growing recognition of the importance of measuring social impact. Civil society organizations are increasingly being asked to demonstrate their effectiveness and accountability to funders, donors, and other stakeholders. In response, organizations are developing innovative approaches to measuring impact, such as outcome mapping, social return on investment (SROI) analysis, and participatory evaluation methods.
Overall, while quantifying social impact is undoubtedly challenging, it is crucial for civil society organizations to assess and communicate their effectiveness. By doing so, these organizations can not only demonstrate their impact but also improve their strategies and leverage resources to create meaningful change in society.
Methods and Tools for Measurement
1. Surveys and Interviews
One of the most common methods for measuring social impact is through surveys and interviews. These tools allow organizations to collect data directly from individuals or communities affected by their programs or initiatives. Surveys can be conducted online, through phone calls, or in-person, and can be tailored to specific demographics or target groups. Interviews, on the other hand, provide an opportunity for in-depth conversations and a deeper understanding of individuals’ experiences and perspectives.
2. Case Studies
Case studies involve conducting thorough research and analysis of a particular program or initiative and its impact on a specific group or community. They often involve interviews, observations, and document analysis to gather qualitative and quantitative data. Case studies provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the social impact of a particular intervention, highlighting both the successes and challenges faced.
3. Social Return on Investment (SROI)
SROI is a framework used for measuring and quantifying the social, environmental, and economic value created by an organization’s activities. It involves assessing the outcomes and impacts of interventions and assigning a monetary value to them. SROI takes into account both financial and non-financial metrics and helps organizations understand the cost-effectiveness and social value generated by their programs.
4. Data Analytics and Visualization
Data analytics and visualization tools enable organizations to collect, analyze, and present data in a visually compelling and easy-to-understand format. These tools can help highlight trends, patterns, and correlations in the data, providing insights into the social impact of interventions. By visualizing data, organizations can effectively communicate their impact to stakeholders and make data-driven decisions to improve their programs.
5. Participatory Evaluation
Participatory evaluation involves engaging the target beneficiaries or community members in the measurement process. This approach ensures that the measurement methods and indicators are relevant and meaningful to the people being assessed. It empowers individuals by giving them a voice in the evaluation process and helps organizations gain a more accurate understanding of the social impact of their initiatives.
6. Impact Assessment Frameworks
Several impact assessment frameworks, such as the Logic Model, Theory of Change, and Results-Based Accountability, provide structured approaches to measuring social impact. These frameworks help organizations identify their goals, map out their strategies, define their indicators, and assess their outcomes and impacts. They provide a systematic and comprehensive way to measure social impact and monitor progress towards desired outcomes.
7. Peer Review and External Evaluation
Peer review and external evaluation involve seeking feedback and assessment from external experts or stakeholders who are not directly involved in the programs or initiatives being evaluated. This method brings an objective perspective to the measurement process and ensures transparency and credibility. Peer review and external evaluation can provide valuable insights and constructive feedback, helping organizations improve their impact measurement practices.
Overall, measuring social impact requires a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, as well as the use of various tools and frameworks. It is important for organizations to select the most appropriate methods and tools based on their specific goals, resources, and target audience to ensure accurate and meaningful measurement of their social impact.
The Importance of Data Analysis
Data analysis plays a crucial role in measuring social impact for civil society organizations. It allows these organizations to make informed decisions and evaluate the effectiveness of their programs and initiatives. By analyzing data, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and correlations that may not be apparent at first glance. This information can then be used to improve their strategies, target resources more effectively, and ultimately achieve greater social impact.
Informing Decision-making
Data analysis provides valuable insights that can inform decision-making processes within civil society organizations. By analyzing data, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the needs and preferences of the communities they serve. This information can help them prioritize their efforts, allocate resources efficiently, and develop targeted interventions. For example, data analysis can reveal which programs are most effective in addressing specific social issues, allowing organizations to focus on those areas and achieve better outcomes.
Evaluating Program Effectiveness
Data analysis allows civil society organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of their programs and initiatives. By analyzing data on indicators such as participant satisfaction, behavioral changes, and community impact, organizations can assess whether their interventions are achieving the desired outcomes. This evaluation process is essential for identifying what works and what doesn’t, allowing organizations to make necessary adjustments and improvements. Through data analysis, organizations can ensure that they are making a meaningful difference in the lives of the communities they serve.
Measuring Social Impact
Data analysis is crucial for measuring social impact, as it helps organizations quantify and communicate their achievements. By analyzing data on various social indicators, organizations can determine the extent to which their programs and initiatives have contributed to positive change. This information can be used to demonstrate accountability to stakeholders, attract funding, and advocate for policy changes. Data analysis provides evidence of the organization’s impact, giving credibility and legitimacy to its work.
In conclusion, data analysis is of paramount importance in measuring social impact for civil society organizations. It enables informed decision-making, allows for the evaluation of program effectiveness, and helps measure and communicate social impact. By harnessing the power of data, these organizations can maximize their efforts and achieve meaningful and lasting change in society.
Case Studies: Successful Impact Measurement
Educational Organization A
One example of successful impact measurement is Educational Organization A, which focuses on providing quality education in underserved communities. To measure their impact, the organization conducts pre- and post-assessments of students’ academic performance, tracking their progress over time. They also collect data on the number of students completing their programs, as well as their college acceptance rates.
Key indicators:
- Academic performance improvement
- Program completion rate
- College acceptance rate
Health Nonprofit B
Another case study is Health Nonprofit B, which aims to improve access to healthcare services in rural areas. As part of their impact measurement strategy, the organization tracks the number of individuals who receive medical services through their clinics and mobile health units. They also collect qualitative data through interviews and surveys to understand the impact of their services on individuals’ health outcomes and overall well-being.
Key indicators:
- Number of individuals receiving medical services
- Qualitative data on health outcomes
- Qualitative data on overall well-being
Environmental Initiative C
Lastly, Environmental Initiative C focuses on promoting sustainable practices and conservation efforts. To measure their impact, they monitor the number of trees planted, the reduction in carbon emissions attributed to their initiatives, and the adoption of sustainable practices by businesses and communities. They also conduct surveys to assess public awareness and behavior change regarding environmental issues.
Key indicators:
- Number of trees planted
- Reduction in carbon emissions
- Adoption of sustainable practices
- Public awareness and behavior change
In conclusion, these case studies highlight the importance of measuring social impact in various sectors. By identifying key indicators and collecting relevant data, organizations can effectively assess their progress and make informed decisions to further their mission and achieve meaningful change.
Lessons Learned: Improving Impact Measurement
Measuring social impact is a vital aspect of evaluating the success of civil society initiatives. However, it is often a complex and challenging task. Over the years, numerous lessons have been learned to improve impact measurement and ensure its accuracy and effectiveness. These lessons can guide organizations and projects in better measuring and understanding their social impact.
1. Clearly define intended outcomes and indicators:
In order to measure impact accurately, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the intended outcomes and indicators before initiating any project or program. This involves conducting a thorough needs assessment and defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This clarity allows for more focused and effective impact measurement.
2. Collect data at multiple points in time:
Measuring impact is not a one-time event. It requires collecting data at multiple points in time to capture changes and trends over the course of a project or program. This longitudinal data allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the impact being made and helps identify any potential gaps or challenges that need to be addressed.
3. Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative data:
Quantitative data provides numerical evidence of impact, such as the number of people reached or the increase in knowledge or skills. However, qualitative data is equally important as it helps capture the deeper, personal experiences and stories of those affected by the program. By combining both types of data, organizations can paint a more holistic picture of their impact.
4. Engage stakeholders in the measurement process:
Engaging stakeholders, including beneficiaries, partners, and local communities, is crucial in improving impact measurement. By involving them in the measurement process, organizations can gather diverse perspectives and insights, which can lead to more accurate and meaningful results. This participatory approach also fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among all stakeholders.
5. Regularly review and adapt impact measurement methods:
Impact measurement is an evolving process that requires continuous learning and improvement. It is important to regularly review and adapt the methods and tools used for measuring impact based on feedback, new research, and emerging best practices. This ensures that impact measurement remains relevant, effective, and aligned with the evolving needs and contexts of civil society initiatives.
In conclusion, improving impact measurement requires a holistic and iterative approach that involves clearly defining outcomes, collecting data over time, using both quantitative and qualitative methods, engaging stakeholders, and adapting measurement methods. By implementing these lessons learned, civil society organizations can enhance their understanding of their social impact and make more informed decisions to drive meaningful change.





