In recent years, the urgency of addressing climate change has become increasingly evident. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and the loss of biodiversity are just some of the consequences of our unsustainable practices. In response, civil society organizations around the world have been playing a crucial role in raising awareness and driving change towards climate justice.
One of the key ways civil society is mobilizing for climate justice is through advocacy and public campaigns. Organizations such as Greenpeace, 350.org, and Extinction Rebellion have been at the forefront of mobilizing public support and pressuring governments and corporations to take action. Through targeted media campaigns, protests, and grassroots organizing, these organizations are raising awareness about the impact and urgency of climate change.
Another crucial role that civil society plays in the fight for climate justice is holding governments and corporations accountable for their actions. By monitoring and reporting on environmental practices, civil society organizations ensure that sustainability commitments are met and that the rights of marginalized communities are protected. Through legal actions and public pressure, civil society is pushing for stronger regulations and policies that prioritize ecological sustainability and social justice.
Furthermore, civil society organizations are working to empower individuals and communities to take action at the local level. Through education and capacity-building programs, they are equipping people with the knowledge and skills to make sustainable choices and advocate for change in their own communities. By fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility, civil society is creating a broader movement for climate justice that goes beyond governmental and corporate actions.
In conclusion, civil society organizations play a critical role in raising awareness and driving change towards climate justice. Through advocacy, holding governments and corporations accountable, and empowering individuals and communities, civil society mobilizes people around the world to take action and create a more sustainable and just future.
Understanding the Climate Crisis
The climate crisis, also known as global warming, refers to the long-term changes in the Earth’s climate system, primarily due to the increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), trap heat from the sun and cause the planet’s surface temperature to rise.
Causes of the Climate Crisis
The climate crisis is primarily caused by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for energy. When these fossil fuels are burned, they release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect. Deforestation and industrial processes such as cement production also release significant amounts of CO2.
Another major contributor to the climate crisis is methane emissions, which primarily come from the production and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that is released during the extraction and transportation of these fossil fuels. Additionally, agricultural practices, such as livestock farming and rice cultivation, also contribute to methane emissions.
Consequences of the Climate Crisis
The climate crisis has severe consequences for both the environment and human societies. Rising global temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, resulting in sea-level rise. This threatens coastal communities and increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Furthermore, the climate crisis also impacts ecosystems and biodiversity. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt ecosystems, leading to the loss of habitats and species extinction. The health and well-being of human populations are also at risk, as the climate crisis can exacerbate food and water insecurity, spread diseases, and worsen air quality.
Addressing the climate crisis requires urgent action from governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals. It involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions through transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing sustainable land-use practices, and promoting energy efficiency. It also involves adapting to the changing climate through measures such as building resilient infrastructure, enhancing disaster preparedness, and protecting natural ecosystems.
The Role of Civil Society
Civil society plays a crucial role in driving change and raising awareness about climate justice. With their ability to mobilize communities, organizations, and individuals, civil society has the power to shape public opinion and influence government policies.
Advocacy and Campaigning: Civil society organizations are at the forefront of advocacy and campaigning efforts to address climate change and environmental issues. They raise awareness about the urgency of climate action through education, media campaigns, and grassroots mobilization. By using their platforms to voice concerns and push for sustainable solutions, civil society plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion.
Monitoring and Accountability: Civil society organizations also play a vital role in monitoring government and corporate actions related to climate justice. They hold governments and corporations accountable for their environmental commitments and push for transparency and accountability in decision-making processes. Through research, documentation, and advocacy, civil society keeps track of the progress and challenges related to climate justice.
Building Resilient Communities: Civil society organizations are often the ones working directly with communities that are most affected by climate change. They play a crucial role in empowering communities through capacity building, education, and helping them adapt to the impacts of climate change. By facilitating community-led initiatives and supporting grassroots solutions, civil society organizations help build resilience and ensure that local voices are heard in climate policy discussions.
Partnerships and Collaboration: Civil society organizations provide a platform for collaboration between different stakeholders to address climate justice. They bring together government agencies, businesses, communities, and individuals to create innovative solutions and promote sustainable practices. Through partnerships and collaboration, civil society fosters dialogue, knowledge exchange, and collective action to create a more sustainable future.
International Advocacy: Civil society organizations also play a vital role in international climate negotiations and advocacy. They participate in climate conferences, engage in lobbying efforts, and provide expertise and perspectives from local communities. By being active and influential participants, civil society organizations ensure that the voices and concerns of those most affected by climate change are heard on a global scale.
In conclusion, civil society plays a multifaceted role in driving change and raising awareness about climate justice. Through advocacy, monitoring, community empowerment, partnerships, and international advocacy, civil society organizations contribute to a more sustainable and just future for all.
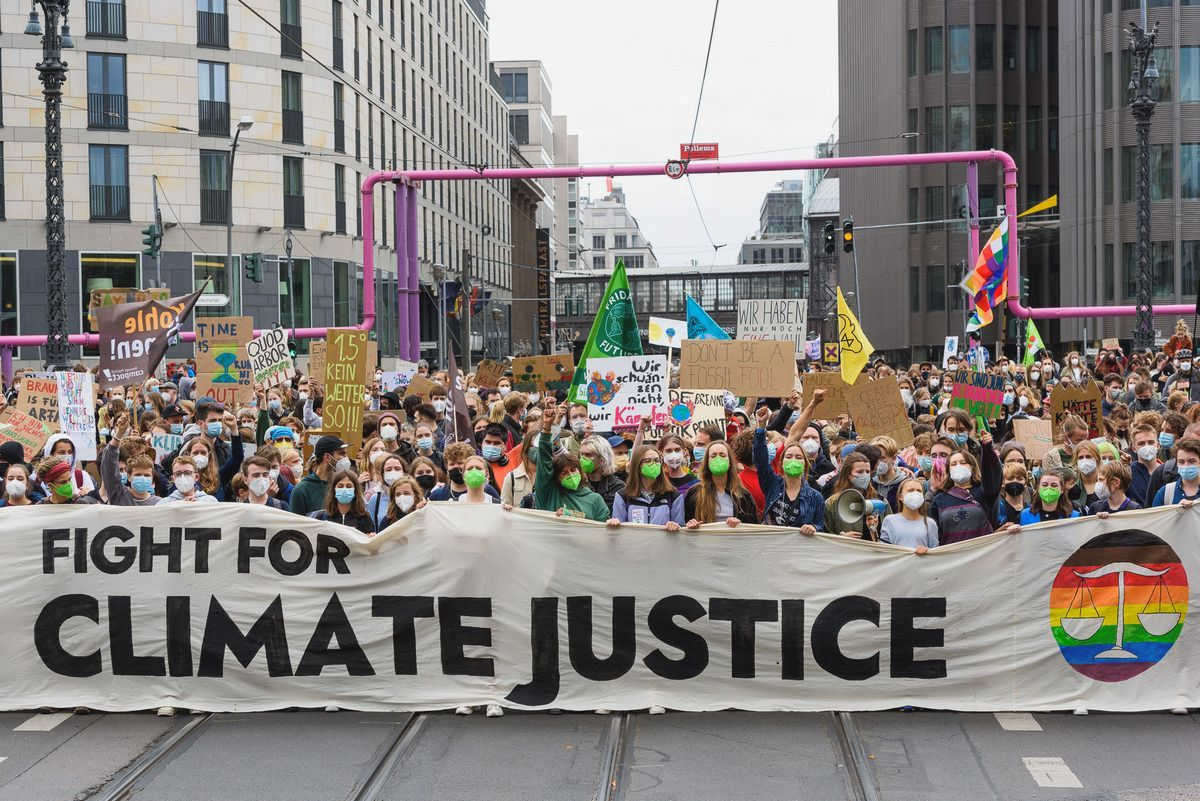
Grassroots Activism and Climate Justice
Grassroots activism plays a crucial role in the fight for climate justice. It involves individuals and local communities coming together to create change from the ground up. These activists recognize the urgent need to address the climate crisis and take matters into their own hands, advocating for policies and practices that prioritize environmental sustainability and social equity.
One of the key aspects of grassroots activism is raising awareness about the impact of climate change on marginalized communities. These activists work to amplify the voices of those most affected by the climate crisis, such as low-income communities and indigenous peoples. By highlighting the disproportionate burden placed on these communities, grassroots activists aim to build empathy and solidarity across society.
Grassroots activists also focus on building sustainable alternatives to current systems that contribute to climate change. They advocate for renewable energy sources, promote local food production and distribution, and push for sustainable transportation solutions. By demonstrating the viability of these alternatives, grassroots activists inspire others to adopt sustainable practices and pressure governments and corporations to make meaningful changes.
Furthermore, grassroots activism is an important driver of mobilization and collective action. These activists organize protests, marches, and grassroots campaigns to put pressure on decision-makers and demand transformative policies and actions. They work to mobilize individuals and communities to unite behind the fight for climate justice, fostering a sense of empowerment and agency among participants.
In conclusion, grassroots activism is essential in the fight for climate justice. It raises awareness, empowers marginalized communities, promotes sustainable alternatives, and mobilizes individuals and communities towards collective action. By working together at the grassroots level, we can drive the systemic changes needed to address the climate crisis and create a more just and sustainable future.
Advocacy and Policy Reform
Advocacy and policy reform are essential components of the efforts to address climate change and achieve climate justice. Civil society organizations play a crucial role in advocating for policy changes that promote sustainability and protect the rights of vulnerable communities.
One of the main focuses of advocacy is pushing for stronger environmental regulations and laws. Civil society organizations work to influence policymakers and raise awareness about the urgency of addressing climate change. They often engage in lobbying activities, conducting research, and providing evidence-based arguments to support their cause.
Advocacy for climate justice also involves working towards the implementation of international agreements and frameworks, such as the Paris Agreement. Civil society organizations participate in international conferences and negotiations to ensure that climate justice principles are included in global policies. They advocate for ambitious emission reduction targets, equitable financial mechanisms, and the protection of human rights in climate action.
In addition to influencing policy at the international level, civil society organizations also engage in advocacy at the national and local levels. They work to build coalitions and partnerships with other stakeholders, such as grassroots movements, indigenous communities, and marginalized groups. These collaborations aim to amplify the voices of those most affected by climate change and ensure that their perspectives are considered in policy-making processes.
Overall, advocacy and policy reform are key strategies for civil society organizations to drive change and mobilize for climate justice. By challenging existing policies and advocating for stronger regulations, these organizations help to create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Youth-led Movements for Climate Action
One of the most inspiring and impactful forces in the fight against climate change is the rise of youth-led movements for climate action. Young people around the world are taking center stage, demanding action from their governments and communities to address the urgent issue of climate change.
These youth-led movements are characterized by their passion, determination, and innovative strategies. They have organized protests, strikes, and demonstrations, drawing attention to the need for immediate and ambitious action to combat climate change. Through social media and online platforms, they have connected with like-minded individuals from different countries, forming a global network of activists united in their mission to protect the planet.
These movements are also pushing for systemic change, recognizing that individual actions alone are not enough to tackle the scale of the climate crisis. They are advocating for policy reforms and holding governments accountable for their climate commitments. By engaging in direct dialogue with policymakers and participating in international climate negotiations, they are amplifying their voices and ensuring that youth perspectives are included in decision-making processes.
Furthermore, youth-led movements are not just demanding action from governments; they are also leading by example in their own communities. They are implementing sustainable practices in their schools, organizing tree-planting initiatives, and promoting renewable energy solutions. By demonstrating the feasibility of climate-friendly actions, they are inspiring others to join the movement and sparking a ripple effect of change.
In conclusion, youth-led movements for climate action are playing a vital role in raising awareness and driving change on the issue of climate justice. Their passion, determination, and innovative strategies are shaping the global dialogue on climate change, demanding immediate and ambitious action from governments and communities alike. By empowering young people to be agents of change, these movements are paving the way for a more sustainable and just future for all.
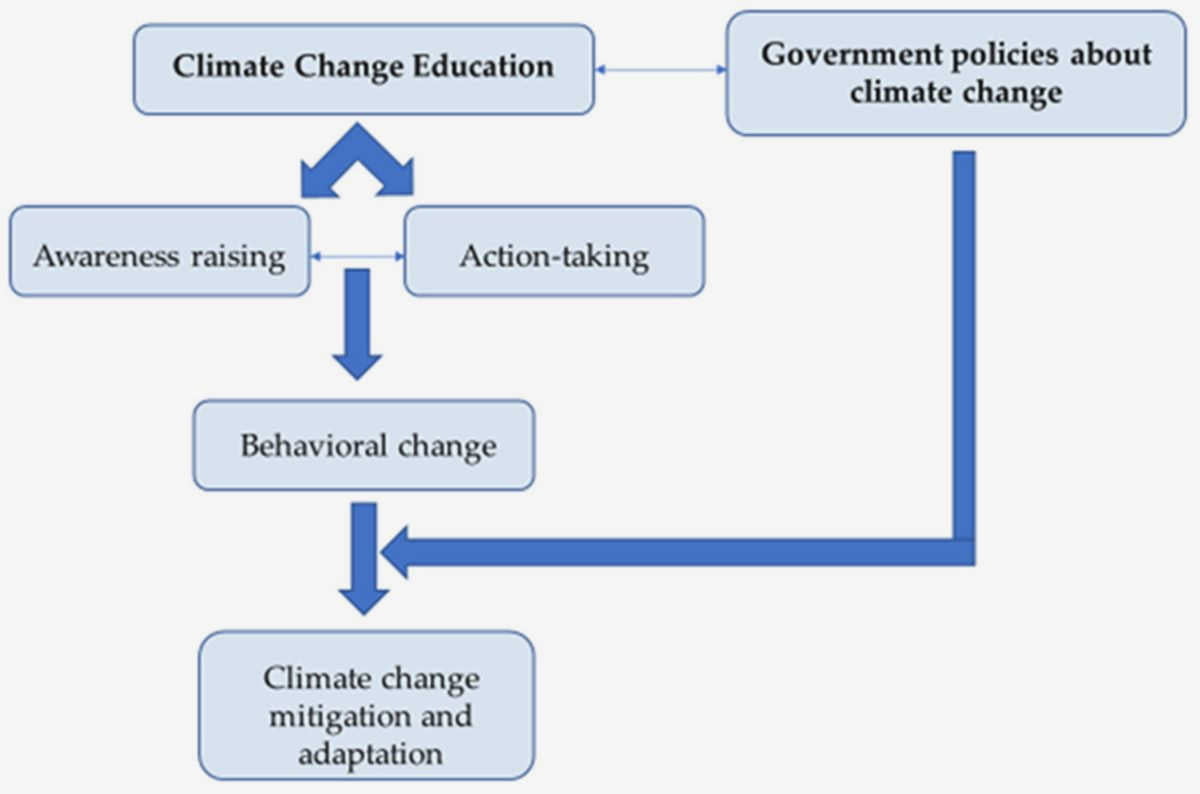
The Power of Education and Awareness
Educating the public about the realities of climate change and raising awareness of its impact is crucial in driving change and mobilizing action. Through education, individuals are empowered to understand the science behind climate change, its causes, and its consequences. This knowledge is essential in dispelling misconceptions and promoting informed decision-making at both the individual and collective levels.
Education for all ages: Initiatives that promote climate change education should target people of all ages, from young children to older adults. By incorporating climate change topics into school curricula, educational institutions can ensure that young people grow up with a strong understanding of the issue and develop a sense of responsibility towards the environment. Moreover, adult education programs can help disseminate knowledge among older populations who may have limited access to information.
Building climate literacy: Climate literacy goes beyond understanding the basic concepts of climate change. It involves fostering critical thinking skills and the ability to critically evaluate information related to climate change. Through climate literacy programs, individuals can learn how to interpret scientific data, assess the credibility of sources, and recognize the interconnectedness between climate change and social justice issues.
Engaging diverse communities: Education and awareness initiatives should strive to engage diverse communities to ensure that the message reaches all sectors of society. By tailoring communication strategies to different cultural backgrounds, languages, and socioeconomic contexts, organizations can effectively communicate the urgency and importance of climate change action to a wide range of audiences.
Collaboration with experts: Collaborating with experts and scientists is essential to ensure the accuracy and credibility of educational materials and awareness campaigns. By involving experts from various fields – including climate science, sociology, and economics – organizations can provide a holistic understanding of climate change and its far-reaching impacts.
Measuring impact: It is important to measure the impact of education and awareness efforts to gauge their effectiveness and make necessary improvements. This can be done through surveys, evaluations, and data collection to assess changes in knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to climate change.
In conclusion, education and awareness play a pivotal role in addressing the challenges of climate change. By equipping individuals with knowledge, promoting critical thinking, and engaging diverse communities, we can empower people to take action and drive meaningful change towards a more sustainable future.
Corporate Accountability and Climate Justice
Corporate accountability is a crucial aspect of the fight for climate justice. As large corporations contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation, it is essential that they are held responsible for their actions and encouraged to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing their carbon footprint, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and mitigating the negative impacts of their operations.
The Role of Transparency
Transparency is key in ensuring corporate accountability. By making information about their environmental impact, emissions, and sustainability efforts publicly available, corporations can be held accountable by civil society organizations and the public. This transparency allows for greater scrutiny and encourages companies to improve their environmental performance.

Advocating for Regulation
In addition to transparency, civil society organizations play a crucial role in advocating for regulations that hold corporations accountable for their actions. They work to push for stricter environmental standards, policies that incentivize sustainable practices, and penalties for non-compliance. By working together with governments, these organizations can drive systemic change that addresses the root causes of climate change and ensures that corporations bear the responsibility for their environmental impact.
Engaging Shareholders
Engaging shareholders is also an important strategy in promoting corporate accountability. Shareholders have the power to influence corporate decision-making and push companies to prioritize sustainability. By advocating for resolutions that require companies to assess and disclose their climate risks, shareholders can hold corporations accountable for their impact on the environment and push for greater action to address climate change.
In summary, corporate accountability is a necessary element in the fight for climate justice. Through transparency, regulation advocacy, and shareholder engagement, civil society organizations can ensure that corporations take responsibility for their environmental impact and work towards a more sustainable future.
Innovations and Technologies for a Sustainable Future
1. Renewable Energy Sources
One of the key innovations for a sustainable future is the development and implementation of renewable energy sources. These sources, such as solar power, wind energy, and hydroelectric power, offer clean and limitless sources of energy that can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Energy-efficient Technologies
Another important area of innovation is the development of energy-efficient technologies. These technologies aim to reduce the energy consumption of various devices and systems, such as buildings, appliances, and transportation. Examples include smart thermostats, energy-efficient LED lighting, and electric vehicles.
3. Green Building Practices
Green building practices focus on constructing and designing buildings that are environmentally friendly and sustainable. This includes using renewable materials, incorporating energy-efficient systems, and implementing designs that maximize natural lighting and ventilation. Green buildings can greatly reduce energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future.
4. Waste Management Solutions
Innovations in waste management solutions are crucial for a sustainable future. This includes adopting recycling programs, developing waste-to-energy technologies, and implementing strategies to reduce waste generation. By properly managing and treating waste, we can minimize pollution, conserve resources, and promote a circular economy.
5. Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of farming while ensuring food security. This includes organic farming methods, agroforestry, and precision agriculture techniques. By promoting sustainable agriculture practices, we can protect soil health, conserve water resources, and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
6. Water Conservation Technologies
Technologies focused on water conservation are essential for a sustainable future, especially in regions facing water scarcity. These technologies include water-efficient irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting, and water recycling and reuse systems. By conserving water resources, we can ensure their availability for future generations.
In conclusion, innovations and technologies play a vital role in shaping a sustainable future. With the development and implementation of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient technologies, green building practices, waste management solutions, sustainable agriculture practices, and water conservation technologies, we can create a more environmentally friendly and resilient world.
Collaboration and Partnerships for Climate Action
In order to effectively address the challenges of climate change, collaboration and partnerships are crucial. Civil society organizations, governments, businesses, and other stakeholders must work together to find sustainable solutions and implement climate action plans.
Civil society organizations play a key role in raising awareness and mobilizing for climate justice. These organizations bring together individuals and communities who are passionate about addressing climate change and work towards creating a more sustainable future. They collaborate with governments, businesses, and other stakeholders to advocate for policy changes, raise funds for climate initiatives, and promote climate education and awareness.
Governments have a significant role in driving climate action. They create policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices and encourage climate-friendly investments. Governments also collaborate with civil society organizations and businesses to develop and implement climate action plans, set carbon emissions targets, and allocate resources for renewable energy projects.
Businesses are increasingly recognizing the need for climate action and are taking steps to reduce their carbon footprint. They are partnering with civil society organizations and governments to develop sustainable business practices, invest in renewable energy, and reduce emissions. Through collaboration, businesses can share best practices and innovations, and work towards a more sustainable and low-carbon economy.
International partnerships are also essential for climate action. Countries around the world must come together to address the global nature of climate change. International organizations, such as the United Nations, facilitate dialogue and collaboration between nations, promote information sharing, and coordinate efforts to mitigate climate change. These partnerships can lead to the development of global climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which aim to limit global warming and support vulnerable communities.
In conclusion, collaboration and partnerships are crucial for effective climate action. Civil society organizations, governments, businesses, and international stakeholders must work together to raise awareness, drive change, and create a more sustainable future for all.
Empowering Local Communities for Climate Resilience
Climate change is a global issue that affects local communities in various ways. To build resilience and adapt to the challenges posed by a changing climate, it is crucial to empower local communities to take action. By providing them with the knowledge, resources, and support they need, we can enable local communities to become more resilient and better prepared to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
One way to empower local communities is through education and awareness-raising initiatives. By educating community members about the causes and consequences of climate change, as well as the actions they can take to reduce their carbon footprint and adapt to a changing climate, we can enable them to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect themselves and their environment.
Another important aspect of empowering local communities for climate resilience is fostering collaboration and cooperation among community members. By creating platforms for dialogue and engagement, we can facilitate the exchange of ideas and experiences, as well as the collective development of strategies and solutions to address local climate challenges. This can help build social cohesion and strengthen community resilience in the face of climate-related risks.
Access to resources and technologies is also crucial for empowering local communities for climate resilience. By providing communities with the necessary resources, such as funds, infrastructure, and technologies, we can enable them to implement climate adaptation and mitigation measures. This can include supporting the installation of renewable energy systems, improving water management practices, and implementing nature-based solutions, among other initiatives.
Overall, empowering local communities for climate resilience requires a multi-faceted approach that combines education, collaboration, and access to resources. By investing in the empowerment of local communities, we can enhance their capacity to adapt to climate change, reduce vulnerabilities, and build a more sustainable and resilient future.





