In an increasingly digital world, where technology is constantly evolving and becoming more integrated into our daily lives, the importance of preserving privacy has become a critical issue for civil society. The rapid advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence, internet of things, and big data analytics, have provided individuals and organizations with unprecedented capabilities to collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of personal data.
However, this technological progress has also raised concerns about the potential misuse of personal information and the erosion of privacy. As governments and corporations continue to collect and analyze data on a massive scale, there is a growing need to establish frameworks and regulations that protect individuals’ privacy rights. Without adequate safeguards, the very fabric of civil society may be eroded, as trust and confidence in institutions and systems are undermined.
One possible solution to this challenge is the use of encryption and other privacy-enhancing technologies. By encrypting personal data and communications, individuals can protect their privacy and ensure that their information remains confidential and secure. This approach empowers individuals to control their own data and decide who has access to it, effectively minimizing the risk of unauthorized surveillance or data breaches.
Another crucial aspect of preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology is the establishment of legal and ethical frameworks. Governments and regulatory bodies need to collaborate with technology companies and civil society organizations to develop comprehensive privacy laws and regulations that strike a balance between privacy rights and the legitimate needs of society. These frameworks should outline clear guidelines on data collection, consent, and usage, as well as provide mechanisms for recourse and redress in case of privacy violations.
Privacy in the Digital Age
In the digital age, privacy has become an increasingly important and complex issue. With the rapid advancement of technology, individuals are constantly generating and sharing vast amounts of personal information online. This has led to concerns about the protection of privacy and the potential for misuse of this information.
The rise of social media and online platforms has changed the way we interact and share information with others. While these platforms offer a variety of benefits, such as connecting with friends and accessing information, they also pose significant privacy risks. Users often unknowingly disclose personal details, such as their location, interests, and habits, which can be exploited by malicious actors.
To address these concerns, there have been calls for greater transparency and control over personal data. Organizations and governments have implemented data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, to provide individuals with more control over their personal information. These regulations require organizations to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting and processing their data.
Additionally, individuals can take steps to protect their privacy online. This includes using strong, unique passwords for online accounts, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about sharing personal information on public platforms. It is also important to regularly review and update privacy settings on social media and other online platforms.
- Being aware of potential risks and educating oneself about data privacy can also help individuals make more informed decisions about sharing personal information online.
- Using virtual private networks (VPNs) and encrypted messaging services can help protect data and communications from unauthorized access.
- Government and technology companies also play a crucial role in preserving privacy in the digital age. They should invest in robust security measures, regularly update privacy policies, and ensure that user data is handled responsibly.
In conclusion, privacy in the digital age is a multifaceted issue that requires a combination of user awareness, regulatory measures, and responsible practices from both individuals and organizations. By taking proactive steps to protect personal information and advocating for stronger privacy regulations, we can strive to maintain privacy in the face of evolving technology.
Threats to Privacy
As technology continues to advance, the threats to privacy become more prevalent and sophisticated. One of the main concerns is the collection and misuse of personal data. Companies and organizations often collect vast amounts of data from individuals, including their personal information, online activities, and even physical movements. This data can be used for various purposes, such as targeted advertising, surveillance, and profiling.
Data breaches pose another significant threat to privacy. As more and more data is stored digitally, it becomes a tempting target for hackers and cybercriminals. A single breach can result in the exposure of sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft and other forms of fraud. Individuals are often unaware of these breaches until it is too late, making it difficult to protect their privacy.
The rise of social media has also contributed to privacy concerns. Many people willingly share personal information on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, but they may not fully understand the consequences. This information can be accessed by advertisers, third-party apps, and even governments, compromising individuals’ privacy and potentially leading to misuse or exploitation.
Furthermore, the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new challenges to privacy. With interconnected devices and smart technologies, personal data is constantly being collected and shared. From smart home devices to fitness trackers, there are countless opportunities for this data to be intercepted or abused. Individuals may unknowingly sacrifice their privacy in exchange for convenience and efficiency.
The lack of regulation surrounding privacy is also a significant threat. Government legislation has not kept pace with technological advancements, leaving individuals and their personal data vulnerable. Without proper safeguards and regulations, privacy breaches are more likely to occur, and individuals have limited recourse to protect themselves.
- Inadequate data protection measures
- Surveillance and monitoring
- Profiling and targeted advertising
- Data trading and selling
- Identity theft and fraud
In summary, the threats to privacy in the face of evolving technology are numerous and complex. From data breaches to social media and IoT, individuals’ personal information is constantly at risk. Without proper regulation and awareness, protecting privacy will continue to be a challenge in the future of civil society.
The Role of Technology
In the context of preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology, it is important to consider the role that technology itself plays in both the erosion and enhancement of privacy. On one hand, technology has facilitated the collection, analysis, and dissemination of vast amounts of personal data, leading to potential privacy breaches. On the other hand, technology can also be harnessed to empower individuals and organizations in protecting privacy.
1. Data Collection and Analysis: The advancements in technology have made it easier than ever to collect and analyze data. With the proliferation of smart devices, sensors, and digital platforms, individuals’ personal information is constantly being gathered and processed. This data can be used by both private companies and governments to gain insights into individuals’ behaviors, preferences, and activities, thereby potentially compromising their privacy.
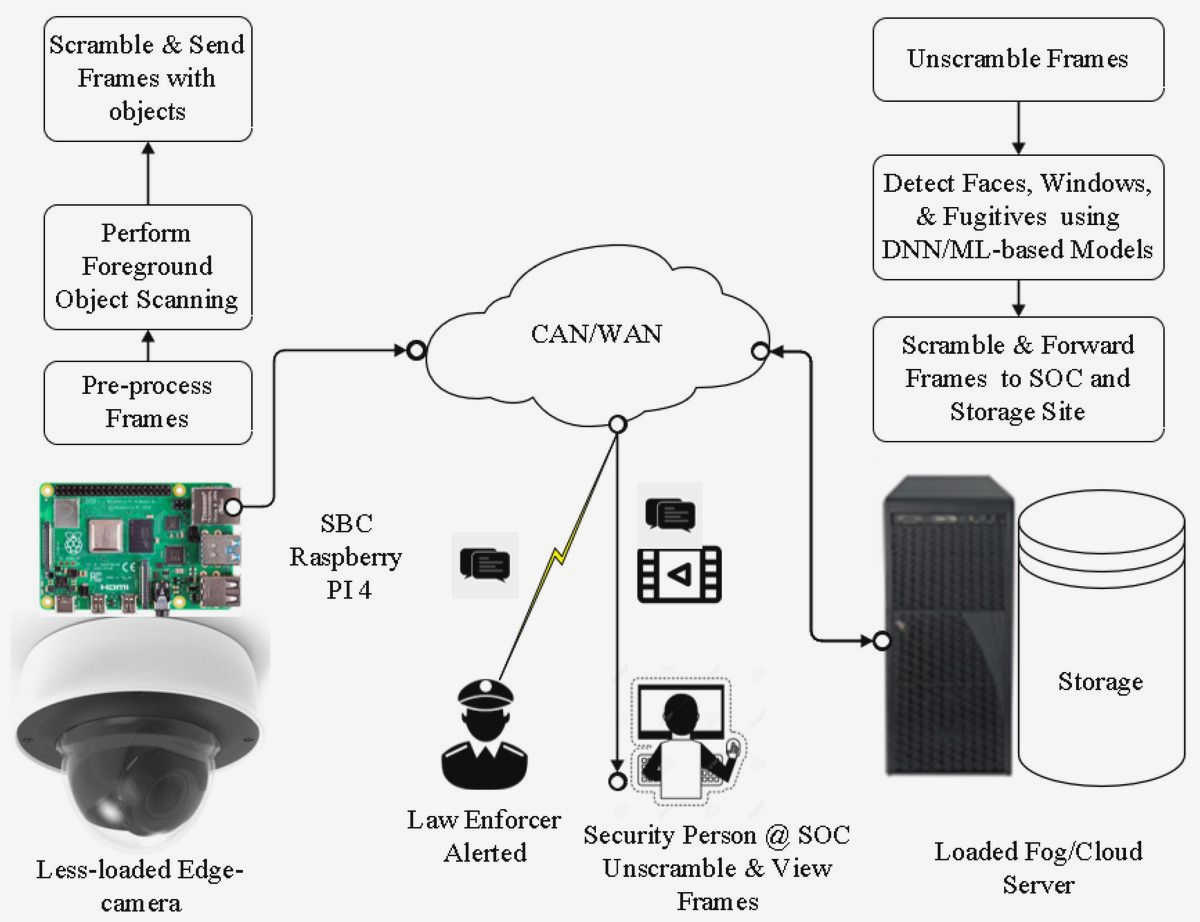
2. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Despite the privacy risks technology presents, it also offers solutions to protect individuals’ privacy. Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) encompass a range of tools and techniques that aim to preserve privacy in the digital age. These include encryption, anonymization, and pseudonymization methods, which allow for secure communication and data protection. PETs also encompass technologies like ad-blockers and browser extensions that help individuals maintain control over their personal information.
3. Balancing Privacy and Innovation: As technology continues to evolve, striking a balance between privacy and innovation becomes crucial. It is important to recognize that privacy and technological progress are not inherently contradictory. Instead, they can complement each other. Innovators need to consider privacy as a fundamental design principle in the development of new technologies. By taking a privacy-first approach, technology can be designed to protect individuals’ personal information while still enabling innovation and progress.
4. Legal and Ethical Frameworks: Technology alone cannot ensure privacy; it requires the establishment of legal and ethical frameworks. Governments play a crucial role in regulating the use of technology and protecting individuals’ privacy rights. The implementation of comprehensive data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), can hold organizations accountable for ensuring individuals’ privacy. Ethical guidelines and standards can also guide the responsible use of technology, ensuring that privacy considerations are integrated into decision-making processes.
5. Education and Empowerment: Ultimately, individuals need to be educated and empowered to protect their privacy in the face of evolving technology. Digital literacy and awareness about privacy risks are essential for individuals to make informed choices about the technologies they use and the data they share. By empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the digital landscape, they can actively participate in preserving their privacy and demanding accountability from technology providers and policymakers.
In conclusion, technology plays a dual role in the future of civil society‘s privacy. While it poses privacy risks through data collection and analysis, it also offers solutions through privacy-enhancing technologies. Striking a balance between privacy and innovation, establishing legal and ethical frameworks, and empowering individuals through education are crucial steps in preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology.
Government Surveillance
In recent years, government surveillance has become a contentious issue in the debate surrounding privacy and civil liberties. With the rapid advancement of technology, governments around the world have gained unprecedented power to monitor and collect data on their citizens.
This surveillance can take many forms, from the widespread collection of metadata through phone calls and internet activity, to the use of advanced surveillance technologies such as facial recognition and artificial intelligence. While governments argue that these measures are necessary for national security and the prevention of crime, many critics argue that they infringe upon the privacy and individual rights of citizens.
One of the major concerns surrounding government surveillance is the potential for abuse of power. When governments have access to vast amounts of personal data, there is the risk that this information could be misused or exploited for political purposes. This has led to calls for increased transparency and accountability in government surveillance programs.
The threat to privacy posed by government surveillance has also sparked a growing movement for encryption and anonymity technologies. Privacy advocates argue that individuals have the right to communicate and browse the internet without the fear of being monitored. Encryption technologies, such as end-to-end encryption, can help protect individuals from government surveillance by securing their communications.
While there are valid arguments for the need for government surveillance in certain cases, it is important to strike a balance between security and privacy. As technology continues to advance, governments must be held accountable for their surveillance practices to ensure that the rights and freedoms of individuals are protected.
Privacy Laws and Regulations
Privacy laws and regulations play a crucial role in protecting individuals’ personal information and ensuring their privacy rights are upheld. These laws govern the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data, and vary from country to country.
The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR, implemented in 2018, is one of the most comprehensive and strict privacy laws in the world. It applies to all EU member states and regulates how organizations handle the personal data of EU citizens. The GDPR requires organizations to obtain explicit consent for data collection, provide transparent privacy policies, allow individuals to access and correct their data, and implement security measures to protect personal information.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA, effective from 2020, is a landmark privacy law in the United States. It grants California residents certain rights over their personal information, such as the right to know what data is being collected, the right to opt out of data sales, and the right to have their data deleted. The CCPA applies to businesses that collect personal data from California residents and meet certain criteria.
International Privacy Laws
In addition to national privacy laws, there are several international agreements and frameworks that aim to protect privacy on a global scale. One example is the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework, which provides a set of principles for member economies to follow in order to promote privacy protection. Another example is the Convention for the Protection of Individuals with regard to Automatic Processing of Personal Data, also known as Convention 108, which is an international treaty that sets out basic principles for privacy protection.
The Role of Privacy Laws in the Future
As technology continues to evolve, privacy laws and regulations will need to adapt to address emerging risks and challenges. This may include enhancing the protection of personal information in the context of artificial intelligence, internet of things, and big data analytics. In addition, there will be a growing need for international cooperation and harmonization of privacy laws to ensure consistent standards across borders.
Corporate Data Collection
Corporate data collection refers to the practice of companies gathering and storing large amounts of information from individuals. With the advancement of technology, corporations have access to an unprecedented amount of personal data, including browsing history, location data, and purchasing habits. This data is often used for targeted advertising, market research, and other business purposes.
Data Mining: Companies use various techniques and technologies to collect and analyze data about their customers. This process, known as data mining, involves extracting patterns, trends, and insights from large datasets. Data mining techniques include machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and statistical analysis.
Privacy Concerns: The widespread collection of personal data raises significant privacy concerns. Many individuals may be unaware of how much information is being collected about them and how it is being used. The data can be used to create detailed profiles of individuals, which may include sensitive information. There is a risk that this data could be misused or accessed by unauthorized individuals, leading to potential harm.
Transparency and Consent: It is important for companies to be transparent about their data collection practices and obtain proper consent from individuals. This includes informing individuals about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. Users should have the ability to opt out of data collection and have their information deleted if they wish.
Regulation and Oversight: To protect individual privacy, there is a need for regulations and oversight of corporate data collection practices. Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in setting guidelines and enforcing compliance with privacy laws. It is important to strike a balance between allowing companies to use data for legitimate purposes while ensuring privacy rights are respected.

Data Security: With large amounts of personal data being collected and stored by corporations, there is a need for robust data security measures. Companies should implement strong encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access. Individuals should also be educated about data security best practices and take steps to protect their own personal information.
Ethics and Accountability: Corporate data collection raises ethical questions about the use and ownership of personal information. Companies should adhere to ethical guidelines when collecting and using data, ensuring that individuals’ rights and privacy are respected. There should also be mechanisms in place for holding companies accountable for any misuse or mishandling of personal data.
In conclusion, while corporate data collection offers many benefits for businesses, it also presents significant privacy concerns. Transparency, consent, regulation, data security, ethics, and accountability are crucial factors in preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology.
Encryption and Data Security
In the era of evolving technology, encryption and data security have become crucial for preserving privacy in civil society. Encryption is the process of encoding information so that it can only be accessed by authorized users. It provides an additional layer of protection for sensitive data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals or hackers to read or interpret.

Data security refers to the measures taken to protect data from unauthorized access, use, or theft. With the increasing dependence on digital systems and the vast amount of data being generated, ensuring data security has become a significant concern. Organizations and individuals need to implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information from breaches and cyberattacks.
Importance of Encryption
Encryption plays a vital role in preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology. It ensures that confidential data remains secure, even if it falls into the wrong hands. By encrypting data, organizations can protect sensitive information such as personal details, financial transactions, and communication from unauthorized access.
Encryption also helps to maintain the integrity of data by preventing unauthorized modifications or tampering. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and fraud.
Types of Encryption
There are different types of encryption techniques that can be used to secure data. These include:
- Symmetric encryption: This technique uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt the data. It is faster but less secure compared to asymmetric encryption.
- Asymmetric encryption: This technique uses two separate keys, a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. It provides a higher level of security but is slower in performance.
- Hashing: Hashing is a one-way encryption technique that converts data into a fixed-size string of characters. It is commonly used for password storage and verifying data integrity.
By implementing robust encryption techniques and data security measures, organizations and individuals can protect their privacy and safeguard confidential information from unauthorized access or misuse in the face of evolving technology.
The Importance of Education
Education is a fundamental aspect of human development and progress. It is the key to unlocking individual potential and empowering individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to society.
Empowering Individuals: Education provides individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in life. It equips them with the tools to think critically, solve problems, and communicate effectively.
Social Mobility: Education plays a crucial role in promoting social mobility and reducing inequalities. It gives individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds the opportunity to improve their lives and break the cycle of poverty.
Promoting Economic Growth: Education is a driver of economic growth and development. It equips individuals with the skills necessary to enter the workforce and contribute to the economy. It also fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, leading to the creation of new businesses and industries.
Building Strong Communities: Education fosters community engagement and active citizenship. It helps individuals develop a sense of belonging and responsibility to their community. It promotes social cohesion and unity, fostering strong and resilient communities.
Preserving Culture and Heritage: Education is essential for preserving culture and heritage. It teaches individuals about their history, traditions, and values, ensuring that they are passed down from generation to generation. It also promotes cultural diversity and understanding, fostering tolerance and respect.
Lifelong Learning: Education is a lifelong process that extends beyond the classroom. It encourages individuals to continue learning and developing their skills throughout their lives. Lifelong learning is essential for personal growth and adapting to the ever-changing world.
In conclusion, education plays a crucial role in the development of individuals and societies. It empowers individuals, promotes social mobility, drives economic growth, builds strong communities, preserves culture and heritage, and encourages lifelong learning. Investing in education is investing in a better future for all.
Balancing Privacy and Innovation
In the evolving digital landscape, striking a balance between privacy and innovation is crucial. On one hand, innovation drives progress, pushes boundaries, and introduces new technologies that enhance our lives in numerous ways. On the other hand, privacy is a fundamental human right that should be protected and preserved. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, it is essential to find a middle ground where innovation can thrive while ensuring privacy remains intact.
One way to strike this balance is through the implementation of privacy-by-design principles. By integrating privacy considerations from the very beginning of the design and development process, organizations can create innovative solutions while minimizing privacy risks. This proactive approach allows for the identification and mitigation of potential privacy issues, fostering trust and ensuring that privacy is prioritized alongside innovation.
Another aspect to consider is transparency. As innovative technologies collect and process vast amounts of personal data, it is crucial for organizations to be transparent about how this data is being used and protected. Clear and user-friendly privacy policies, coupled with accessible consent mechanisms, empower individuals to make informed decisions about their personal information. By promoting transparency, organizations can foster a culture of trust and ensure that individuals have confidence in the innovative solutions being offered.
Collaboration is also key in balancing privacy and innovation. Governments, civil society organizations, and the business sector must work together to develop privacy frameworks and regulations that support innovation while protecting individuals’ rights. By engaging in ongoing dialogue, stakeholders can address the evolving challenges posed by technology and find innovative solutions that respect privacy and push the boundaries of what is possible.
Ultimately, society must recognize that privacy and innovation are not mutually exclusive. By embracing privacy as a foundational principle in the design and development of innovative solutions, we can create a future where individuals’ privacy rights are upheld, while still benefiting from the advancements that technology brings. It is through this delicate balance that we can preserve privacy in the face of evolving technology and ensure a future that is both innovative and respectful of individuals’ privacy rights.
The Future of Privacy and Technology
The rapid advancement of technology has brought many benefits to society, but it has also raised concerns about the future of privacy. As technology continues to evolve, it is becoming increasingly challenging to preserve privacy in the face of new innovations.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, Big Data, and the Internet of Things have the potential to gather vast amounts of personal information. This raises questions about how this data will be used and protected. The future of privacy will depend on how society and policymakers address these challenges.
Risks to privacy
One of the main risks to privacy in the future is the collection and use of personal data by both governments and corporations. With the increasing reliance on technology in various aspects of our lives, our personal information is being stored and shared more than ever before.
This proliferation of data creates opportunities for surveillance, profiling, and discrimination. Without proper safeguards and regulations, individuals may find their privacy invaded and their personal information misused.
Potential solutions
Preserving privacy in the face of evolving technology will require a multi-faceted approach. Educating individuals about their rights and the risks associated with sharing personal information is crucial. Additionally, strengthening privacy laws and regulations to keep pace with technological advancements is essential.
Technological solutions, such as encryption and anonymization, can also play a role in protecting privacy. These can help individuals control access to their personal data and mitigate the risks of unauthorized use or disclosure.
Collaboration and cooperation between governments, corporations, and civil society organizations will be crucial to finding a balance between technological innovation and privacy protection. By working together, it is possible to develop policies and practices that enable the benefits of technology to be realized while still respecting individual privacy rights.





