Voting rights play a crucial role in shaping the level of civil society involvement. The ability to vote is not only a fundamental democratic right, but it also empowers individuals to participate in the decision-making process of their society. When citizens have the right to vote and actively engage in the political process, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their community.
Engaged civil society involvement encompasses a range of activities, including but not limited to, volunteering, activism, advocacy, and community participation. Voting rights act as a catalyst for individuals to become more actively involved in these endeavors. When people have a say in electing their representatives, they feel a greater stake in the outcome of political decisions and are more likely to take an active role in shaping their communities.
Furthermore, voting rights contribute to the development of a more inclusive and representative civil society. When all members of a society have equal access to the voting booth, it ensures that diverse perspectives and interests are taken into account during decision-making processes. This inclusivity strengthens civil society by promoting dialogue, compromise, and the formation of diverse coalitions.
To fully understand the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement, it is essential to recognize the historical struggles for suffrage and the ongoing efforts to protect and expand voting rights. Throughout history, marginalized groups, such as women, racial and ethnic minorities, and the economically disadvantaged, have fought for their right to vote. By acknowledging these struggles and working to ensure equal access to the ballot box, society can strengthen the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement.
The Importance of Voting Rights
Voting rights are the foundation of a healthy democracy, allowing individuals to have a say in the governance of their country. They ensure that every citizen has an equal opportunity to participate in the decision-making process and shape the future of their nation.
One of the key benefits of voting rights is the ability to elect representatives who will advocate for the interests and needs of the people they serve. By casting a vote, citizens have the power to choose leaders who align with their values and goals, and who will work towards creating a better society for all.
Voting rights also promote inclusivity and diversity within the political system. When everyone has the right to vote, it ensures that marginalized communities have a voice and can influence policies that directly impact their lives. This encourages greater representation of diverse perspectives and experiences, leading to more equitable outcomes.
Furthermore, voting rights are crucial for holding elected officials accountable. By participating in elections, citizens can express their approval or disapproval of a government’s actions. This serves as a check on the power of those in office and encourages transparency, responsiveness, and accountability in governance.
Overall, voting rights are essential for maintaining a vibrant and engaged civil society. They empower individuals to actively participate in shaping the policies and direction of their country, creating a democratic system that is truly representative of its citizens.
History of Voting Rights
Voting rights have evolved over time, often reflecting the changing social and political landscape of a nation. In many countries, the right to vote was initially restricted to a specific group of individuals, such as wealthy landowners or males of a certain age. However, as societies progressed and ideas of equality and democracy took hold, steps were taken to expand voting rights to a wider population.
One of the early milestones in the history of voting rights was the Magna Carta signed in 1215. While primarily focused on limiting the power of the monarch, it also included provisions that protected the rights of freemen, including their right to justice and representation. This laid the foundation for the concept of political participation and influenced future movements for expanded voting rights.
The struggle for voting rights continued throughout history, with different countries and regions achieving milestones at different times. For example, the United States saw significant developments in voting rights in the 19th and 20th centuries. The 15th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, ratified in 1870, prohibited the denial of voting rights based on race, while the 19th Amendment, ratified in 1920, granted women the right to vote.
In other parts of the world, voting rights were expanded as a result of anti-colonial movements and struggles for independence. Countries that were previously colonized often had to fight for equal rights and representation within their own governments. This included advocating for universal suffrage, enabling all adult citizens to have a say in the political process.
It is important to recognize that the history of voting rights is not stagnant and continues to evolve. Efforts are still being made in many regions to combat voter suppression and ensure equal access to the ballot box for all citizens. The fight for voting rights is closely tied to the broader fight for civil rights and societal equality, as an engaged civil society plays a vital role in shaping the political landscape of a nation.
Current Challenges and Controversies
1. Voter Suppression
One of the major challenges facing the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement is voter suppression. This refers to various tactics aimed at discouraging or preventing certain groups of people, such as minorities or low-income individuals, from exercising their right to vote. Examples of voter suppression tactics include strict voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, reducing early voting hours, and gerrymandering.
2. Disinformation and Misinformation
In the age of social media and online platforms, another challenge is the spread of disinformation and misinformation regarding voting rights and elections. False information and conspiracy theories can easily go viral, confusing and misleading voters. This creates a major barrier to engaged civil society involvement, as individuals may be hesitant to participate in the democratic process if they are unsure about the accuracy and integrity of the information they receive.
3. Partisan Polarization
Partisan polarization is another significant challenge that affects the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement. In highly polarized societies, individuals and political parties may prioritize their own interests over the greater good, leading to the adoption of policies and practices that undermine voting rights, such as restrictive voter registration laws or biased redistricting. This polarization can also hinder efforts to promote active participation in civil society, with individuals becoming more focused on partisan battles rather than cooperative engagement.
4. Access and Equity
Ensuring equal access to the voting process is essential for fostering engaged civil society involvement. However, disparities in access and equity persist in many countries, including limited polling locations in certain areas, long wait times, and inadequate language assistance for non-native English speakers. These barriers can disproportionately affect marginalized communities, limiting their ability to participate fully in the democratic process and engage meaningfully in civil society activities.
5. Technological Challenges
The rapid advancement of technology brings both opportunities and challenges to the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement. While technological innovations can enhance accessibility and efficiency in the voting process, they also raise concerns about cybersecurity and the potential for hacking or other forms of interference. Building secure and reliable systems while embracing technological advancements is crucial to maintaining trust in the electoral process and encouraging active participation in civil society.
In conclusion, there are various challenges and controversies that impact the connection between voting rights and engaged civil society involvement. Overcoming these challenges and addressing these controversies is vital for promoting inclusivity, accountability, and active participation in the democratic process.
Voting Rights and Democracy
Ensuring voting rights is a fundamental aspect of promoting and sustaining a thriving democracy. The ability for all eligible citizens to access the ballot and participate in elections is crucial for the functioning of a democratic society. Without the protection of voting rights, certain groups may be marginalized and unable to have their voices heard in the decision-making process.
Historical Context: Throughout history, the fight for voting rights has been a significant part of broader movements for social justice and equality. From the suffrage movement, which campaigned for women’s right to vote, to the civil rights movement, which fought for voting rights for African Americans, the struggle to ensure equal access to the ballot has shaped the course of democracy.
Importance of Voting Rights:
Voting rights empower individuals and provide them with a platform to express their political opinions and preferences. By allowing citizens to vote, a democracy can more accurately represent the will of the people and ensure that decision-making processes are reflective of diverse perspectives. When voting rights are protected, individuals can actively participate in shaping the policies and direction of their government.
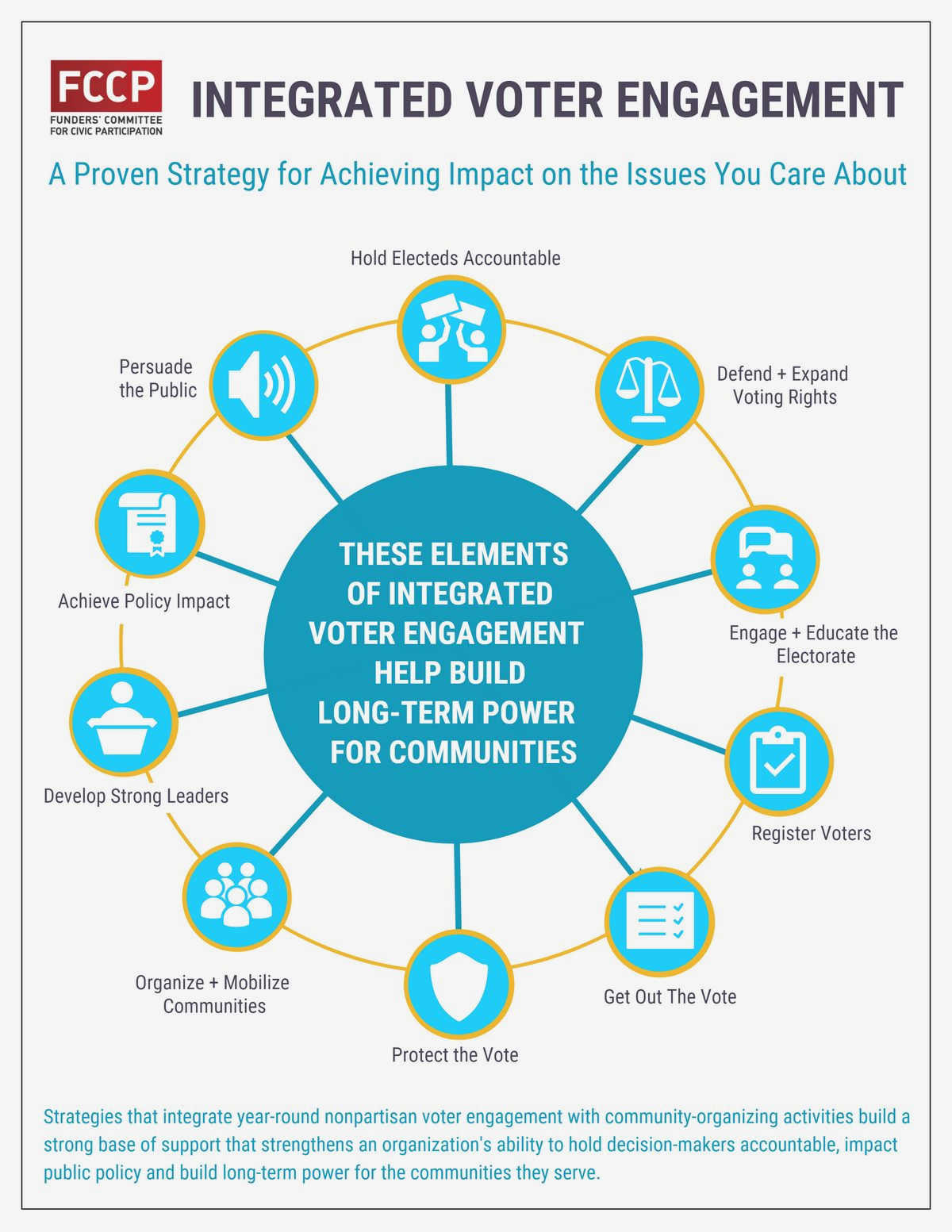
Expanding Democracy: Protecting and expanding voting rights is essential for fostering an engaged civil society and promoting citizen participation in the political process. When everyone has equal access to the ballot, it encourages individuals to become more informed, engaged, and invested in the issues that affect them and their communities. This, in turn, leads to a more vibrant and inclusive democracy.
Challenges and Solutions:
Despite the importance of voting rights, challenges persist in some societies. These challenges can include voter suppression tactics, inadequate access to polling stations, and various forms of discrimination. To address these challenges, it is crucial to implement comprehensive voter protection laws, such as ensuring early voting options, expanding voting opportunities, and combating voter ID laws that disproportionately affect marginalized communities.
Engaged Civil Society: Voting rights and civil society involvement are interconnected. When individuals can exercise their right to vote, it encourages them to become more engaged in their communities and advocate for policies that align with their values. Civil society organizations play a vital role in educating and mobilizing individuals to ensure that voting rights are protected and that all eligible citizens can participate in the democratic process.
Ensuring Equal Access to Voting
Voting is a fundamental right in a democratic society, and it is crucial to ensure equal access for all eligible citizens. Equal access to voting means that every citizen has the opportunity to exercise their right to vote without any barriers or discrimination.
1. Voter Registration
One of the key steps in ensuring equal access to voting is to have a fair and accessible voter registration process. This includes providing multiple methods of registration, such as online, mail, and in-person options, to accommodate different needs and preferences of citizens. Additionally, efforts should be made to make the voter registration process simple, clear, and easily understandable for all individuals.
2. Voting Locations
Equal access also means having convenient and accessible voting locations. This includes ensuring that polling places are located in areas that are easily reachable for all citizens, including those with disabilities or limited mobility. It is important to have a sufficient number of polling places to prevent overcrowding and long waiting times, which can deter some voters from participating.
3. Voter Education
Voter education plays a crucial role in ensuring equal access to voting. It is important to provide comprehensive and accessible information about the voting process, including registration deadlines, identification requirements, and how to navigate the ballot. This education should be provided through various channels, including online resources, community outreach programs, and partnerships with schools and educational institutions.
4. Language Access
To ensure equal access to voting, it is essential to provide language access services for voters who have limited proficiency in English. This includes translating voting materials, such as ballots and voter guides, into different languages spoken by significant portions of the population. Additionally, providing bilingual poll workers and language assistance hotlines can help bridge the language barrier and ensure that every eligible voter can fully participate in the democratic process.
5. Voter ID Laws
When implementing voter ID laws, it is important to strike a balance between preventing voter fraud and ensuring equal access to voting. ID requirements should be reasonable and should not impose unnecessary burdens on eligible voters, especially those from marginalized communities who may face difficulties in obtaining the required identification documents. Efforts should be made to provide free or low-cost options for obtaining valid IDs.
In conclusion, ensuring equal access to voting is essential for a vibrant and engaged civil society. By implementing fair and accessible voter registration processes, providing convenient and accessible voting locations, offering comprehensive voter education, ensuring language access, and enacting reasonable voter ID laws, we can strengthen our democracy and empower all eligible citizens to exercise their right to vote.
The Role of Civil Society Organizations
Civil society organizations (CSOs) play a crucial role in ensuring the functioning of a healthy and active democracy. As non-governmental organizations, they operate independently from the government and are driven by a mission to promote the interests and rights of citizens in a democratic society.
Advocacy and Public Awareness
One of the primary roles of CSOs is to advocate for the rights of citizens and raise public awareness about important social and political issues. Through their advocacy efforts, CSOs help mobilize citizens and encourage them to actively engage in the democratic process, including participating in elections and exercising their voting rights.
CSOs often conduct public education campaigns, organize events and demonstrations, and provide information to the public about their rights and responsibilities as citizens. By raising awareness and engaging citizens, CSOs contribute to the development of an informed and engaged civil society that actively participates in shaping the decisions that affect their lives.
Monitoring and Accountability
CSOs also play a critical role in monitoring the actions of government institutions and ensuring accountability. They act as watchdogs, keeping a close eye on government activities to ensure they are in line with democratic principles and respect the rights of citizens.
CSOs often conduct research, gather evidence, and publish reports on various issues, such as electoral processes, human rights violations, and government transparency. Through their monitoring efforts, CSOs provide valuable information to the public and hold the government accountable for its actions.
Furthermore, CSOs often collaborate with other stakeholders, such as media outlets and international organizations, to amplify their voices and increase their impact in advocating for change. Their work contributes to the overall transparency and integrity of the democratic system.
Capacity Building and Empowerment
In addition to advocacy and monitoring, CSOs also focus on capacity building and empowerment of citizens. They provide training programs, workshops, and resources to empower individuals and communities to actively participate in the democratic process.
Through these initiatives, CSOs aim to increase civic knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and support the formation of grassroots movements. By equipping citizens with the tools and knowledge necessary to engage in democratic processes, CSOs contribute to the development of an active and engaged civil society that values and exercises its voting rights.
Overall, civil society organizations play a vital role in a well-functioning democracy. Their advocacy efforts, monitoring activities, and capacity building initiatives contribute to the promotion of an informed and engaged civil society that actively participates in the democratic process and ensures the protection of voting rights.
Promoting Voter Education and Engagement
1. Increasing Awareness of Voting Rights
One of the key aspects of promoting voter education and engagement is increasing awareness of voting rights. Many people are unaware of their rights when it comes to voting, which can lead to a lower voter turnout. To address this issue, it is important to provide educational materials and resources that explain the voting process, voter registration requirements, and the rights and responsibilities of voters.

2. Empowering Underrepresented Communities
Another important aspect of promoting voter education and engagement is empowering underrepresented communities. These communities often face barriers to voting, such as lack of transportation, language barriers, or a history of voter suppression. By providing targeted outreach and resources to these communities, we can help ensure that all eligible voters have the opportunity to participate in elections and have their voices heard.
3. Providing Accessible and Nonpartisan Information
Providing accessible and nonpartisan information is crucial in promoting voter education and engagement. It is important that the information about candidates, their positions, and the issues at stake is presented in a clear and unbiased manner. This can help voters make informed decisions and feel confident in their choices. Additionally, using language and formats that are accessible to a diverse range of voters, including those with disabilities or limited English proficiency, is essential to ensuring equal access to information.
4. Encouraging Youth Participation
Encouraging youth participation in the electoral process is vital for promoting voter education and engagement. Many young people may not be familiar with the voting process or the impact their vote can have. By implementing comprehensive civics education programs in schools, we can equip young people with the knowledge and skills necessary to become informed and engaged voters. In addition, youth-focused voter registration drives and campaigns can help encourage young people to register to vote and participate in elections.
5. Collaborating with Community Organizations
Collaborating with community organizations is an effective strategy for promoting voter education and engagement. By partnering with local nonprofits, community centers, and advocacy groups, we can leverage their existing networks and resources to reach a wider audience. These partnerships can also help ensure that voter education efforts are tailored to the specific needs and concerns of the community, leading to increased voter turnout and engagement.
Voting Rights and Representation
One of the fundamental aspects of democracy is the principle of representation, where citizens have the right to elect individuals who will represent their interests and make decisions on their behalf. This process is facilitated through voting rights, which give individuals the power to choose their leaders and participate in the democratic process.
Voting rights play a crucial role in ensuring that all citizens have a voice in the governance of their countries. They ensure that every eligible individual has the opportunity to express their opinions and preferences through the democratic process. This inclusivity is essential for a just and equitable society, as it allows for diverse perspectives to be considered and represented.
Access to voting
However, voting rights are meaningless if individuals do not have equal access to the voting process. In many countries, certain marginalized groups may face barriers that limit their ability to exercise their right to vote. These barriers can include restrictive voter ID laws, limited access to polling stations, or suppression tactics that disproportionately impact specific communities.
Efforts must be made to ensure that every eligible citizen has equal access to the voting process. This includes implementing policies and practices that make it easier for individuals to register to vote, providing ample and accessible polling locations, and combating voter suppression tactics. By removing these barriers, societies can ensure that all citizens have an equal opportunity to participate in the democratic process.
Representative democracy
Voting rights are also crucial for the functioning of representative democracy. When individuals exercise their right to vote, they are choosing representatives who will make decisions on their behalf. These elected officials are expected to represent the interests and values of their constituents, making the democratic process more accountable and responsive to the people.
Effective representation requires not only the right to vote but also the presence of diverse voices in positions of power. This means that efforts must be made to ensure that individuals from all walks of life, including marginalized communities, have the opportunity to run for office. By promoting diversity and inclusivity in the political arena, societies can ensure that the needs and concerns of all citizens are taken into account.
In conclusion, voting rights are an essential aspect of democracy and ensure that citizens have a voice in the governance of their countries. Equal access to voting and representation of diverse voices are important principles that must be upheld to maintain a fair and inclusive democratic society.
Voting Rights and Social Justice
Voting rights play a crucial role in ensuring social justice within a society. They provide individuals with the power to participate in the democratic process and have their voices heard. By giving every citizen an equal opportunity to vote, regardless of their race, gender, or socioeconomic status, voting rights promote equality and fairness.
When voting rights are protected and accessible to all, it helps to prevent the marginalization and discrimination of certain groups. In a society where everyone has the right to vote, individuals from all backgrounds can come together to elect leaders who represent their interests and promote policies that foster social justice.
However, when voting rights are restricted or tampered with, it can have severe consequences for social justice. Voter suppression tactics, such as stringent voter ID laws, gerrymandering, or the purging of voter rolls, disproportionately impact minority communities and low-income individuals. These measures can effectively silence certain voices and prevent them from exercising their right to vote.
Protecting and expanding voting rights is therefore crucial for achieving social justice. It ensures that all members of society have a say in shaping their community and country. By promoting voter education and awareness, advocating for fair voting practices, and fighting against voter suppression, we can work towards a more just and equitable society for all.
The Future of Voting Rights and Civil Society Involvement
The future of voting rights and civil society involvement is a critical issue that will shape the democratic processes and social fabric of our societies. As we move forward, it is essential to prioritize the protection and expansion of voting rights to ensure equal access and participation for all citizens.
Voting rights are fundamental to a healthy democracy and serve as a cornerstone of civic engagement. However, these rights have historically been contested and denied to certain groups, such as racial and ethnic minorities, women, and young people. Moving forward, it is crucial to address these historic injustices and work towards eliminating voter suppression tactics, such as restrictive voter ID laws and gerrymandering.
Civil society involvement plays a crucial role in advocating for voting rights and holding governments accountable. Civil society organizations, including grassroots movements and non-profit organizations, have been instrumental in driving positive change and fighting for equal rights. Moving forward, it is essential to foster a culture of active citizenship and encourage civil society involvement in the democratic process.
The role of technology
Technology will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of voting rights and civil society involvement. Advances in digital tools and platforms can make voting more accessible, secure, and convenient. Online voter registration systems, electronic voting machines, and secure online voting platforms are examples of how technology can enhance the democratic process.
Furthermore, technology can also facilitate greater civil society involvement by enabling easier communication, collaboration, and mobilization. Social media platforms and online organizing tools have already proven to be powerful tools for grassroots movements and civil society organizations.
Collaboration and education
Collaboration and education will be crucial in shaping the future of voting rights and civil society involvement. It is important to bring together stakeholders from various sectors, including government, civil society organizations, and technology companies, to work towards common goals.
Education is also vital in empowering citizens and fostering a culture of active engagement. Promoting civic education in schools and providing accessible information on voting rights and the democratic process can help create an informed and engaged citizenry.
In conclusion, the future of voting rights and civil society involvement depends on collective efforts to protect and expand these rights, leverage technology for positive change, and promote collaboration and education. By prioritizing these principles, we can create a more inclusive and participatory democracy for all.





