The right to vote is a fundamental pillar of modern democratic societies, providing citizens with the opportunity to express their preferences and shape the direction of their government. However, the journey towards universal suffrage has been a long and arduous one, marked by both progress and setbacks.
Historically, the right to vote has been restricted to a privileged few, often based on criteria such as wealth, property ownership, or gender. Throughout the centuries, marginalized groups fought tirelessly for their right to participate in the democratic process, challenging the existing power structures and demanding equality and representation.
With the advent of the suffrage movement in the 19th and early 20th centuries, significant strides were made towards expanding voting rights. Women’s suffrage became a focal point of this movement, as women fought for recognition as equal citizens and demanded the right to vote. Gradually, countries around the world began to recognize women’s suffrage, granting them the right to participate in political decision-making.
Despite such advancements, many obstacles remain in the path towards universal suffrage. Voter suppression, the deliberate and systematic effort to hinder certain groups from exercising their right to vote, continues to be a significant challenge. Various methods, such as restrictive voter ID laws, gerrymandering, and unequal access to polling stations, disproportionately affect marginalized communities, perpetuating inequalities in the democratic process.
In conclusion, while progress has been made in the development of the right to vote in modern society, obstacles and challenges persist. The struggle for universal suffrage continues as marginalized groups fight for equal representation and the elimination of barriers to political participation. It is crucial that societies recognize and address these obstacles to ensure a truly democratic and inclusive system that upholds the principles of equality and representation for all.
Understanding the Historical Background of Voting Rights
The history of voting rights is closely tied to the evolution of democratic societies. Throughout history, the right to vote has been a constant source of struggle and contention, as different groups of people have fought for inclusion and equal representation in the electoral process.
One of the earliest examples of voting rights can be traced back to ancient Greece, where a direct form of democracy known as Athenian democracy was practiced. However, it’s important to note that this form of democracy was limited to adult male citizens, excluding women, slaves, and non-citizens from the right to vote.
Fast forward to the 18th and 19th centuries, significant progress was made towards expanding voting rights. The American Revolution, for example, helped solidify the idea that government should be based on the consent of the governed, leading to the extension of voting rights to property-owning white men. Over time, these restrictions began to be challenged by various social movements, such as the women’s suffrage movement and the civil rights movement, which aimed to include women, African Americans, and other marginalized groups in the electoral process.
The struggle for voting rights has been marked by both victories and setbacks. The 19th Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1920, granted women the right to vote, a major milestone in the fight for gender equality. Similarly, in South Africa, the end of apartheid in 1994 brought about universal suffrage, allowing all citizens to vote regardless of their race.
However, voting rights are still contested in many parts of the world. In some countries, certain populations, such as indigenous peoples or individuals with felony convictions, are systematically excluded from voting. Additionally, voter suppression tactics, such as voter ID laws and gerrymandering, continue to undermine the democratic process.
In conclusion, understanding the historical background of voting rights helps to shed light on the progress that has been made in ensuring political inclusion and representation. It also highlights the ongoing challenges and obstacles that need to be overcome in order to achieve true universal suffrage.
The Origins of Suffrage
The concept of suffrage, or the right to vote, has a long and complex history that can be traced back to ancient civilizations. While the notion of democracy and popular participation in decision-making has been present in various forms throughout history, the formalization of suffrage as a fundamental right took shape over time.
One of the earliest examples of suffrage can be found in ancient Athens, where adult male citizens were granted the right to vote in the 5th century BCE. This early form of suffrage, however, was limited to a small subset of the population based on gender, age, and citizenship status.
Throughout medieval Europe, the idea of suffrage became intertwined with the rise of representative institutions such as parliaments and local assemblies. Over time, certain privileges were granted to different social classes, allowing them to participate in the political process to varying degrees. However, these rights were often tied to wealth, land ownership, or aristocratic status, making suffrage a privilege rather than a universal right.
The modern concept of suffrage, as we understand it today, began to develop during the Enlightenment era in the 18th century. Influenced by growing demands for equality and individual rights, philosophers and political thinkers such as John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau argued for the inclusion of all individuals in the political process, regardless of social status or wealth.
It was the French Revolution in the late 18th century that marked a significant turning point in the history of suffrage. The revolutionary government, aiming to create a new system based on popular sovereignty, introduced the concept of universal male suffrage. This meant that all adult men, regardless of wealth or status, were granted the right to vote. However, this new form of suffrage still excluded women from participating in the political process, highlighting the ongoing struggle for gender equality in suffrage rights.
Evolution of Voting Rights Through Centuries
The concept of voting rights has evolved significantly over the centuries, reflecting the changing perceptions of democracy and equality. In ancient times, voting rights were often restricted to a select few individuals, such as wealthy landowners or ruling elites. These limited voting rights meant that the majority of the population, including women and marginalized groups, were unable to participate in the democratic process.
However, with the rise of progressive ideas and movements, the concept of voting rights began to expand. The Magna Carta, signed in 1215, recognized the rights of certain groups, such as barons and church officials, to participate in decision-making processes. This marked an important milestone in the development of voting rights, as it acknowledged the need for broader representation.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the idea of universal suffrage gained traction, advocating for the notion that all adult citizens should have the right to vote. This concept was a driving force behind the American and French Revolutions, which sought to establish governments that reflected the will of the people. While these movements initially focused on extending voting rights to white men, they set a precedent for future struggles for suffrage.
The 20th century witnessed significant advancements in the expansion of voting rights. In many countries, women fought for and gained the right to vote during this time. The suffragette movement, led by courageous women such as Emmeline Pankhurst and Susan B. Anthony, played a pivotal role in ensuring gender equality in voting. Additionally, the civil rights movement in the United States fought against racial discrimination and successfully pushed for legislative changes that prohibited voter suppression based on race.
Today, voting rights continue to be a subject of debate and evolution. Efforts are being made to ensure that marginalized communities, such as ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, and people with disabilities, have equal access to the voting process. Furthermore, discussions on lowering the voting age and exploring alternative voting methods, such as online voting, reflect the ongoing quest to make the democratic system more inclusive and representative of the diverse populations it serves.

In conclusion, the evolution of voting rights throughout history reflects society’s changing attitudes towards democracy and equality. From limited rights for select groups to the ongoing struggle for universal suffrage, voting rights have come a long way. However, there are still obstacles to overcome in order to ensure that every individual has an equal opportunity to participate in the democratic process.
The Importance of Universal Suffrage in Democracy
1. Ensuring Equality and Representation
Universal suffrage, which guarantees the right to vote for all adult citizens, is a cornerstone of democracy. By extending voting rights to all members of society, regardless of their race, gender, or social status, universal suffrage ensures equality and representation. It allows every citizen to have a voice and participate in the decision-making process of their country.
2. Fostering Accountability and Responsiveness
Universal suffrage plays a crucial role in fostering accountability and responsiveness in a democratic society. When all citizens have the right to vote, elected officials are more accountable to the people they represent. They are incentivized to listen to their constituents’ concerns, address their needs, and work towards the betterment of society. This leads to a more responsive government that is more likely to prioritize the well-being of its citizens.
3. Promoting Social Cohesion and Stability
Inclusive voting rights contribute to social cohesion and stability within a democratic society. When all citizens are allowed to participate in elections and have a say in the decision-making process, it helps to bridge societal divides and build a sense of unity. Universal suffrage promotes the idea that every voice matters, reducing the potential for social unrest and fostering a more cohesive and harmonious society.
4. Safeguarding Human Rights and Freedoms
Universal suffrage is closely linked to the protection of human rights and freedoms. By granting every citizen the right to vote, it reinforces the principles of liberty, equality, and justice. It ensures that individuals have the power to shape the policies and laws that govern them, preserving their fundamental rights and freedoms. Universal suffrage serves as a safeguard against the violation of human rights and guarantees that the government remains accountable to its citizens.
5. Enhancing the Legitimacy of the Government
Universal suffrage enhances the legitimacy of the government. When individuals are granted the right to vote, they feel a sense of ownership and investment in their country’s governance. This leads to greater trust and confidence in the government, as citizens believe that their voices are being heard and their interests are being represented. By ensuring broad participation in the electoral process, universal suffrage strengthens the legitimacy of the government and its decisions.
In conclusion, universal suffrage is of paramount importance in a democracy. It provides equal representation, fosters accountability and responsiveness, promotes social cohesion, safeguards human rights and freedoms, and enhances the legitimacy of the government. By upholding the principles of universal suffrage, societies can ensure a fair and inclusive democratic system that reflects the will and aspirations of the people.
Ensuring Equality and Representation
In modern society, ensuring equality and representation in the right to vote is crucial for fostering a fair and just democracy. This means that every eligible citizen, regardless of their race, gender, socioeconomic status, or any other characteristic, should have an equal opportunity to participate in the democratic process and have their voice heard.
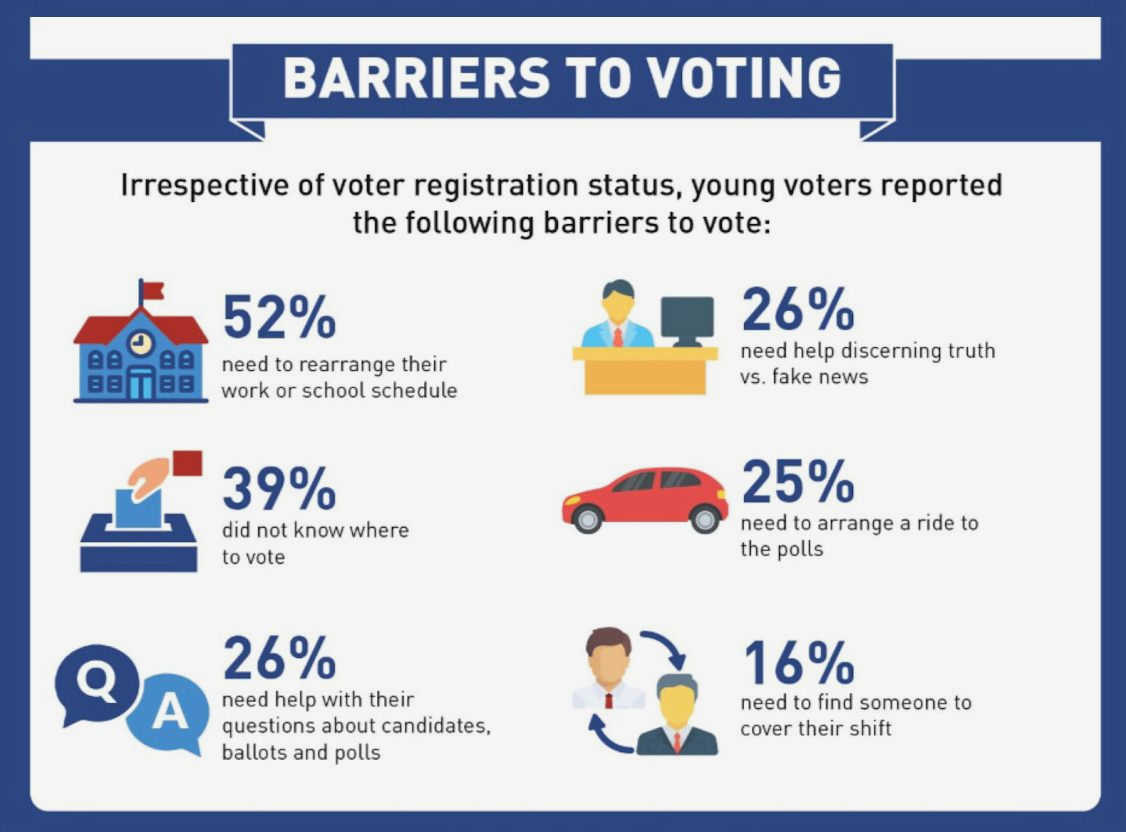
One way to ensure equality and representation in the right to vote is by implementing inclusive voter registration processes. This involves simplifying and streamlining the voter registration process to make it more accessible and user-friendly for all citizens. Governments and election officials can take steps such as implementing online voter registration systems and offering registration assistance to individuals who may face barriers in the process.
Another important aspect of ensuring equality and representation is by addressing voter suppression tactics. These tactics, such as strict voter ID laws, voter intimidation, and gerrymandering, can disproportionately affect marginalized communities and limit their ability to exercise their right to vote. Governments and policymakers need to actively work towards eliminating these barriers and creating an environment where every citizen feels empowered and encouraged to vote.
Furthermore, promoting civic education and engagement is crucial for ensuring equality and representation in the right to vote. By providing individuals with knowledge about the importance of voting, the electoral process, and various candidates and issues, they can make informed choices and actively participate in elections. This can be done through educational campaigns, public forums, and outreach programs that aim to engage citizens, especially those from underrepresented communities.

In addition, it is essential to prioritize the representation of diverse voices in political leadership. This means supporting and encouraging individuals from different backgrounds to run for office and actively working towards overcoming barriers that may hinder their participation. By electing leaders who can empathize with and advocate for various communities, we can ensure that everyone’s interests and concerns are taken into account when making decisions that impact society as a whole.
Ultimately, ensuring equality and representation in the right to vote is a continuous and ongoing process that requires the collective efforts of governments, policymakers, and citizens. By continuously working to address barriers, promote inclusivity, and empower individuals to exercise their right to vote, we can create a society where everyone has an equal opportunity to shape their future and contribute to the democratic process.
Empowering Marginalized Communities
Empowering marginalized communities is crucial in ensuring that everyone has equal access to exercising their right to vote. Marginalized communities, such as minority groups, lower-income individuals, and those with disabilities, have historically faced barriers that have limited their ability to participate in the democratic process.
One way to empower marginalized communities is by providing voter education and outreach programs specifically tailored to their needs. These programs can help individuals understand their rights, navigate the voter registration process, and address any concerns or challenges they may face. By equipping marginalized communities with the knowledge and resources they need to participate, we can help bridge the gap and ensure that their voices are heard.
Another important aspect of empowering marginalized communities is addressing systemic barriers that disproportionately affect them. This can include advocating for changes to voter ID laws, which can disproportionately impact minority groups and lower-income individuals who may face challenges in obtaining the necessary identification. Additionally, efforts should be made to improve accessibility for individuals with disabilities, such as providing accessible polling locations and alternative voting methods.
Empowering marginalized communities also extends beyond the election process itself. It involves addressing underlying social and economic inequalities that contribute to their marginalization. This can include advocating for policies that address income inequality, systemic racism, and discrimination, which can have a direct impact on individuals’ ability to exercise their right to vote.
In conclusion, empowering marginalized communities is essential in ensuring that the right to vote is truly accessible to everyone. Through targeted voter education programs, addressing systemic barriers, and advocating for social and economic equality, we can help empower marginalized communities and create a more inclusive and democratic society.
Challenges and Obstacles to the Right to Vote
The right to vote is a fundamental pillar of democracy, allowing citizens to have a voice in the government’s decision-making process. However, this right has not always been easily accessible, and many individuals and groups have faced challenges and obstacles when trying to exercise their voting rights.
Voter Suppression
One of the major challenges to the right to vote is voter suppression, which involves intentional efforts to prevent certain individuals or groups from voting. This can be achieved through various means, such as implementing strict voter ID laws, reducing early voting periods, purging voter rolls, and gerrymandering electoral districts. These tactics disproportionately affect marginalized communities, including racial and ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, and young people, suppressing their ability to participate in the democratic process.
Disenfranchisement of Felons
Another obstacle to the right to vote is the disenfranchisement of individuals with felony convictions. In many countries, convicted felons are permanently or temporarily stripped of their voting rights. This practice disproportionately affects communities of color, as they are more likely to be targeted by the criminal justice system. Denying formerly incarcerated individuals the right to vote perpetuates their marginalization and hinders their reintegration into society.
Voting Barriers for People with Disabilities
People with disabilities often face significant barriers when attempting to exercise their right to vote. Physical accessibility to polling stations can be inadequate, limiting the ability of individuals with mobility impairments to cast their vote independently. Additionally, voting materials and processes are frequently not accessible to individuals with visual or hearing impairments. These barriers prevent people with disabilities from fully participating in the electoral process and having their voices heard.
Political and Economic Exclusion
Political and economic exclusion can also pose obstacles to the right to vote. In some cases, individuals who are socioeconomically disadvantaged may not have the resources or time to participate in the electoral process fully. Furthermore, marginalized groups, such as indigenous communities or LGBTQ+ individuals, may face discrimination or lack of representation in the political arena. These forms of exclusion restrict their ability to engage in the democratic process and influence government policies that directly affect their lives.
In conclusion, while the right to vote is a fundamental aspect of democracy, numerous challenges and obstacles continue to hinder its full realization. Addressing voter suppression, felon disenfranchisement, barriers for people with disabilities, and political and economic exclusion is crucial to ensuring equal and inclusive access to the right to vote for all individuals and groups in modern society.
Voter Suppression Tactics
Voter suppression refers to the various tactics that are used to discourage or limit the participation of certain groups of voters in elections. These tactics are intended to disproportionately impact specific individuals or communities in order to suppress their ability to exercise their right to vote. Voter suppression can take many forms and has been a persistent issue throughout history.
Purging voter rolls
One common tactic used for voter suppression is the purging of voter rolls. This involves the removal of individuals from the voter registration lists based on certain criteria, such as inactive voting status or discrepancies in their voter information. While purging is intended to maintain accurate voter rolls, it has been used in some cases to disproportionately target certain communities, such as minority or low-income voters.
Strict voter ID laws
Another common tactic is the implementation of strict voter ID laws. These laws require voters to present a valid form of identification in order to cast their vote. While the intention behind these laws is to prevent voter fraud, studies have shown that they can disproportionately impact minority and low-income communities, who may face difficulties in obtaining the required identification.
Reducing early voting opportunities
Restrictions on early voting opportunities can also contribute to voter suppression. By limiting the number of days or hours available for early voting, some individuals may find it more difficult to participate in the electoral process. This can have a disproportionate impact on working individuals, who may not have the flexibility to take time off from work to vote on Election Day.
Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, the manipulation of electoral district boundaries to favor one political party, can also be seen as a form of voter suppression. By drawing district lines in a way that concentrates or dilutes the voting power of certain groups, gerrymandering can effectively reduce the influence of certain communities and undermine fair representation.
Overall, voter suppression tactics serve to undermine the principles of democracy and restrict individuals’ ability to participate in the electoral process. Recognizing and addressing these tactics is crucial for the protection of democracy and ensuring that every eligible voter can exercise their right to vote.
Disenfranchisement of Certain Groups
The right to vote is a fundamental aspect of democracy, providing citizens with the opportunity to have their voices heard and participate in the decision-making process. However, throughout history, certain groups have been systematically disenfranchised, denying them this essential right.
One group that has historically faced disenfranchisement is women. For many years, women were excluded from voting in most countries around the world. It was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that women’s suffrage movements gained traction and led to the recognition of their right to vote. Today, although women have made significant progress in terms of political representation, gender disparities still exist, and women continue to face obstacles in fully exercising their right to vote.
Another group that has been disproportionately disenfranchised is racial and ethnic minorities. Throughout history, racialized discrimination and systemic racism have been used to deny certain groups the right to vote. From slavery to Jim Crow laws, various practices and policies have been employed to suppress the voices of racial and ethnic minorities. While significant strides have been made in combating voter suppression, ongoing challenges such as gerrymandering and voter ID laws continue to disproportionately affect these communities.
Additionally, individuals with disabilities may also face barriers to exercising their right to vote. Inaccessible polling stations, lack of accommodations, and discriminatory attitudes can prevent people with disabilities from fully participating in the electoral process. Efforts to improve accessibility and provide support services have been made, but more needs to be done to ensure equal access to voting for all individuals with disabilities.
In conclusion, while progress has been made in recognizing and protecting the right to vote, certain groups continue to face disenfranchisement and obstacles. It is crucial for societies to address these disparities and work towards creating inclusive and equitable electoral systems that guarantee the full participation of all citizens.
Voting Rights in the Digital Era
The digital era has brought about significant advancements in various aspects of society, including the way we exercise our right to vote. With the widespread availability of the internet and digital technologies, voting processes have become more accessible and convenient for many individuals.
Enabling Accessibility
One of the key benefits of voting in the digital era is the increased accessibility it provides. Online voting platforms make it easier for individuals with physical disabilities or those who are unable to travel to a polling station to exercise their right to vote. This ensures that no one is left out of the democratic process due to their mobility limitations.
Enhancing Participation
The digital era has also created new opportunities for citizens to participate in the voting process. Online voter registration systems allow individuals to easily register to vote from the comfort of their own homes, eliminating the need for lengthy paperwork and unnecessary bureaucratic hurdles. This has the potential to increase voter turnout and engagement, as it simplifies the process and makes it more accessible to a wider range of people.
Addressing Security Concerns
While the digitalization of voting processes offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges in terms of security. Ensuring the integrity of online voting systems is crucial to prevent fraud or hacking attempts. Governments and electoral authorities need to implement robust cybersecurity measures and protocols to safeguard the voting process and protect the privacy of voters.
Internet Access and Inequality
While the digital era has the potential to revolutionize voting, it is important to recognize that not everyone has equal access to the internet and digital technologies. The lack of internet connectivity or technological literacy can create barriers for certain groups, such as elderly citizens or individuals living in rural areas. Efforts must be made to bridge this digital divide and ensure that voting processes are inclusive and accessible to all members of society.
Conclusion
The digital era has brought significant changes to the way we exercise our right to vote. While it offers numerous benefits, such as increased accessibility and participation, it also comes with challenges related to security and inequality. By harnessing the potential of digital technologies while addressing these concerns, societies can work towards creating a more inclusive and democratic voting system.
The Rise of E-Voting
E-voting, also known as electronic voting, has emerged as a potential solution to many of the challenges and obstacles associated with traditional voting methods. With the advancements in technology, e-voting has gained popularity in modern society as a convenient and efficient way to cast votes.
One of the key advantages of e-voting is its accessibility. With traditional voting methods, individuals often face barriers such as physical disabilities, geographical constraints, and long waiting lines at polling stations. E-voting eliminates these obstacles by allowing voters to cast their ballots remotely, using devices such as computers or smartphones. This ensures that everyone, regardless of their physical location or limitations, can participate in the democratic process.
Furthermore, e-voting offers increased accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional paper-based voting. With electronic systems, the risk of human error, such as miscounting or mishandling of ballots, is significantly reduced. Additionally, e-voting allows for faster tabulation of results, eliminating the need for time-consuming manual counting processes.
However, despite its potential benefits, the rise of e-voting also raises concerns regarding security and privacy. Cybersecurity threats and the potential for electoral fraud have become major issues in the implementation of electronic voting systems. It is crucial for governments and organizations to invest in robust security measures to protect the integrity of e-voting systems and ensure the confidentiality of voters’ information.
In conclusion, the rise of e-voting presents both opportunities and challenges in modern society. While it offers convenience, accessibility, and efficiency, precautions must be taken to address concerns regarding security and privacy. As technology continues to advance, it is important to strike a balance between embracing e-voting as a modern voting solution and safeguarding the democratic process.
Ensuring Security and Accessibility in Online Voting
As societies increasingly rely on technology, the process of voting has also undergone significant changes. Online voting has emerged as a potential solution to increase accessibility and convenience for voters, but it also presents unique challenges in ensuring both security and accessibility.
Security Challenges
One of the key concerns with online voting is maintaining the security and integrity of the voting process. Ensuring that the online voting system is protected from hacking and fraud is crucial to maintain public trust in the results. Various measures can be taken to enhance the security of online voting platforms, such as implementing encryption mechanisms, multi-factor authentication, and robust firewalls to prevent unauthorized access.
Additionally, regular security monitoring and audits should be conducted to detect any vulnerabilities or potential breaches. It is essential to collaborate with cybersecurity experts to continuously improve the security infrastructure and stay ahead of emerging threats in the digital landscape.
Accessibility Challenges
While online voting has the potential to make the voting process more accessible, it is vital to address the accessibility challenges that certain groups may face. Not everyone has access to reliable internet or the necessary technology, which can create a digital divide and exclude marginalized populations from participating in online voting.
To ensure accessibility, governments and election authorities should consider providing alternative methods for those without internet access, such as in-person voting or mail-in ballots. Additionally, efforts should be made to educate and raise awareness among underrepresented communities about the availability and benefits of online voting.
An inclusive approach is essential to guarantee that everyone has equal access to exercising their right to vote, regardless of their socio-economic background or technological capabilities.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, online voting presents an opportunity to improve the voting process. However, it is crucial to address the security and accessibility challenges to ensure the integrity of the results and the inclusivity of the process. By implementing robust security measures and providing alternative voting methods, online voting can become a reliable and accessible option for modern societies.





